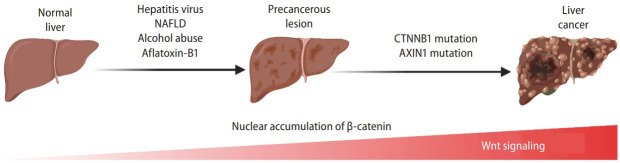
Figure 3.
Wnt signaling in liver cancer. Dynamic activation of β-catenin and Wnt signaling-related gene mutations from risk factor exposure to final liver cancer. With the precancerous lesions induced by hepatitis virus, NAFLD, alcohol assumption, or aflatoxin-B1, genetic and epigenetic alteration (e.g., mutations in the CTNNB1 or AXIN1 genes) lead to the accumulation and nuclear translocation of β-catenin, resulting in initiating liver cancer development. Created with BioRender.com. NAFLD, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.