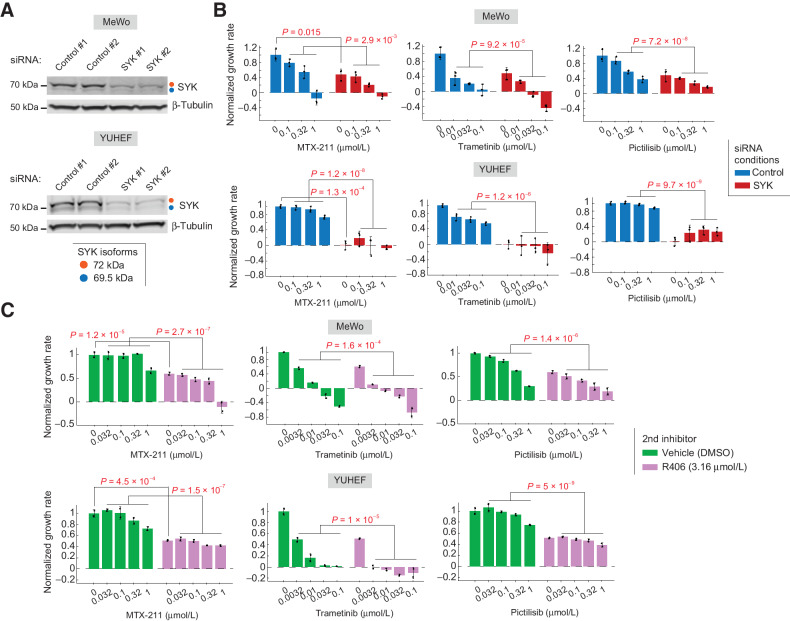
Figure 4.
SYK inhibition or depletion reduces the growth of NF1LoF melanoma cells and increases their sensitivity to both PI3K and MEK inhibitors. A, SYK protein levels assessed by WBs in MeWo (top) and YUHEF cells (bottom) following treatment with siRNAs targeting SYK isoforms or with nontargeting (control) siRNA for 72 hours. Antibodies were costained on the same blot. Each siRNA experiment was performed in two independent replicates. B, Normalized growth rates measured in MeWo (top) and YUHEF (bottom) cells following 72 hours treatment with indicated concentrations of MTX-211, trametinib, or pictilisib (all dissolved in DMSO as vehicle) in the presence of siRNAs targeting SYK or nontargeting (control) siRNA (for 72 hours). Data are presented as mean values ± SD calculated across n = 3 replicates. Statistical significance of the effect of SYK siRNA (vs. control siRNA) in the absence of all inhibitors was determined by two-sided, two-sample t test. Statistical significance of the effect of SYK siRNA (vs. control siRNA) in the presence of inhibitors at three indicated concentrations was determined by two-way ANOVA. C, Normalized growth rates measured in MeWo (top) and YUHEF (bottom) cells following 7-day treatments with indicated concentrations of MTX-211, trametinib, or pictilisib in combination with either R406 (at 3.16 μmol/L) or vehicle (DMSO). Data are presented as mean values ± SD calculated across n = 2 replicates. Statistical significance of the effect of R406 (vs. DMSO) in the absence of other inhibitors was determined by two-sided, two-sample t test. Statistical significance of the effect of R406 (vs. DMSO) in the presence of other inhibitors at four indicated concentrations was determined by two-way ANOVA.