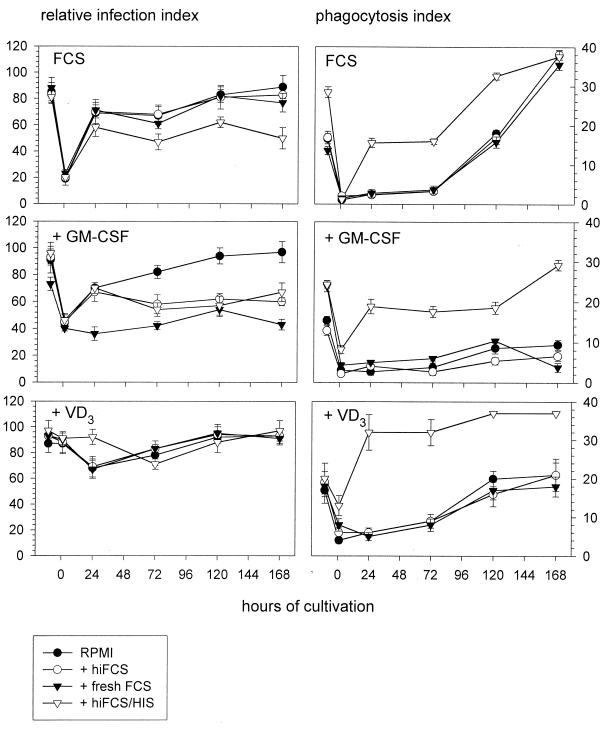
FIG. 3.
Uptake of differently opsonized brucellae by human monocytes and MDM. Uptake of Brucella was compared for freshly isolated, nonadherent monocytes (pre-0-h time point) and monocytes which were allowed to adhere for 1 h (0-h time point) and kept in culture for up to 7 days (24-, 72-, 120-, and 168-h time points). At each time point indicated, phagocyte aliquots were challenged with GFP-expressing B. suis for 20 min and chased for another 30 min. The effects of different supplements to the monocyte culture medium (10% hiFCS [FCS]), FCS with 500 U of GM-CSF per ml [+ GM-CSF]), or FCS with 100 nM VD3 [+ VD3]) and different challenging media (RPMI alone [RPMI] or RPMI containing either 10% hiFCS [+ hiFCS], fresh FCS [+ fresh FCS], or hiFCS with 5 μl of human anti-Brucella immune serum [+ hiFCS/HIS]) were compared. Infection was quantified by count of monocyte-associated fluorescent bacteria. Results are expressed as means ± standard deviations for duplicate samples from one of two experiments with monocytes from different donors which gave comparable results.