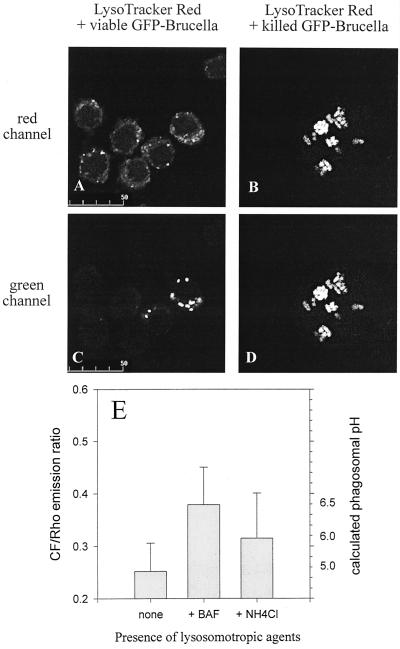
FIG. 7.
Measurement of phagosomal pH in Brucella-infected murine macrophage-like cells. (A to D) J774.A1 cells were challenged with antibody-opsonized, viable (A and C) or heat-killed (B and D) GFP-expressing Brucella for 45 min and chased for another 90 min in the presence of the acidophilic reagent LysoTracker Red. Depicted are paired images in the red (A and B) and green (C and D) channels for visualization of LysoTracker Red and GFP-expressing Brucella, respectively. Even at the high concentration of 1 μM used here, LysoTracker Red colocalizes only weakly and inconsistently with viable Brucella but to the full extent with heat-killed Brucella. These features were observed throughout all infected cells in duplicate experiments. (E) J774.A1 cells were challenged with antibody-opsonized, viable CF- and Rho-labeled Brucella for 45 min and chased for another 90 min in the absence or presence of either 100 nM bafilomycin A1 (BAF) or 30 mM ammonium chloride. Results are expressed as means ± standard deviations for four pairs of CF-Rho images of duplicate experiments; the phagosomal pH was calculated from an in situ calibration curve of the CF/Rho emission ratio versus buffers with defined pHs. Heat-killed brucellae gave the same results as viable ones (data not shown).