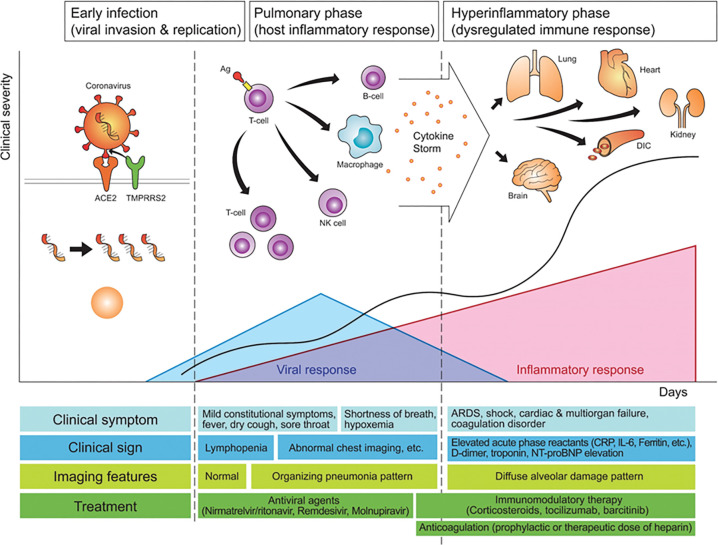
Figure 1:
Diagram shows how pathogenetic evolution of COVID-19 pneumonia correlates with clinical and imaging features and management. The early infection stage occurs at the time of inoculation. During this stage, SARS-CoV-2 binds to its target using the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor and transmembrane protease serine 2 (TMPRRS2) and multiplies in the host cells. In the second stage, the pulmonary phase, viral multiplication and localized inflammation in the lungs occur and viral pneumonia is developed. In a minority of patients with COVID-19, the disease may progress to the most severe stage, the hyperinflammatory phase. An uncontrolled systemic inflammatory response resulting from the cytokine storm occurs at this stage. Pink triangle indicates inflammatory response, blue triangle indicates viral response, and black line indicates clinical severity. Areas under trigon represent chronological changes in the intensity of responses. Ag = antigen, ARDS = acute respiratory distress syndrome, CRP = C-reactive protein, DIC = disseminated intravascular coagulation, IL-6 = interleukin-6, NT-proBNP = N-terminal prohormone of brain natriuretic peptide.