Figure 3:
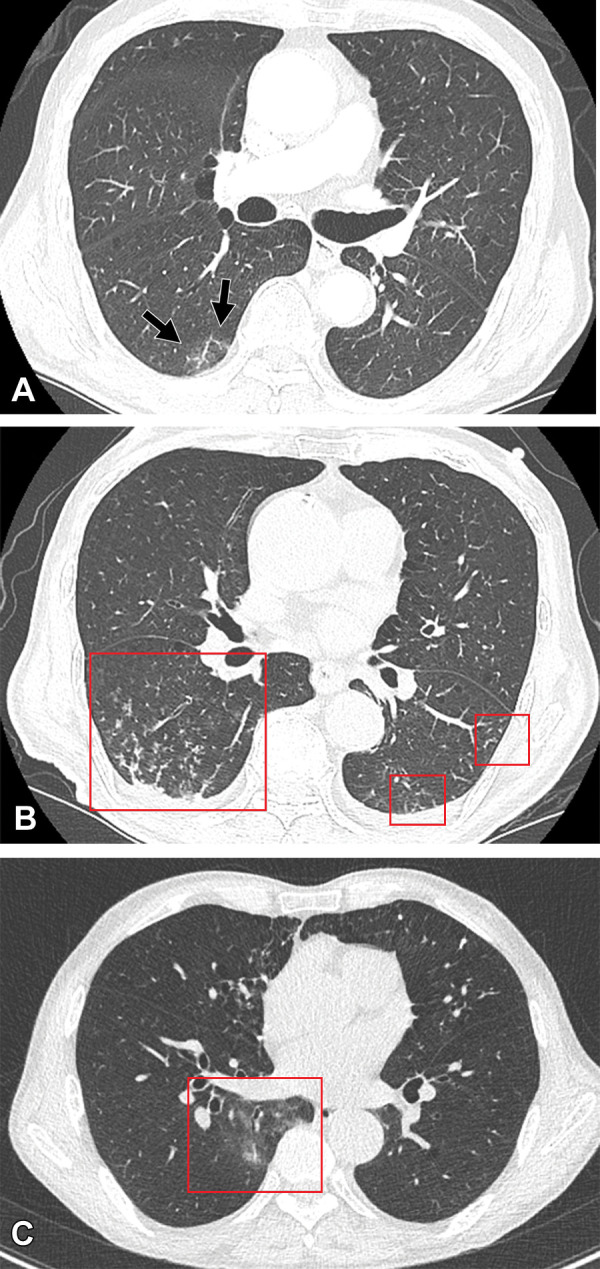
Cases of SARS-CoV-2 reinfection and breakthrough infection during an Omicron BA.5 subvariant–predominant period. (A, B) CT scans (lung window) in an 82-year-old man with COVID-19 reinfection during an Omicron BA.5 subvariant predominant period. The patient had a history of prior Omicron BA.1 subvariant infection and cerebrovascular accident. (A) Transverse nonenhanced CT scan obtained at bronchus intermedius level at the time of Omicron BA.1 subvariant (his first infection) shows focal area of ground-glass opacity (GGO) in superior segment of right lower lobe (arrows). CT findings were classified as “indeterminate” according to the RSNA chest CT classification system. (B) Transverse nonenhanced CT scan obtained at the level of basal trunks at the time of reinfection of Omicron BA.5 subvariant 4 months after the first infection shows poorly defined centrilobular nodules in the dependent portions of bilateral lower lobes (squares). CT findings were classified as “atypical” according to the RSNA chest CT classification system. (C) CT scan (lung window) of breakthrough infection of SARS-CoV-2 during an Omicron BA.1 subvariant–dominant period in a 76-year-old man with a history of hypertension and pulmonary tuberculosis who had received his COVID-19 booster. Transverse nonenhanced CT scan obtained at level of inferior pulmonary vein shows focal area of poorly defined GGO (square) in the right lower lobe. CT findings were classified as “indeterminate” according to the RSNA chest CT classification system.
