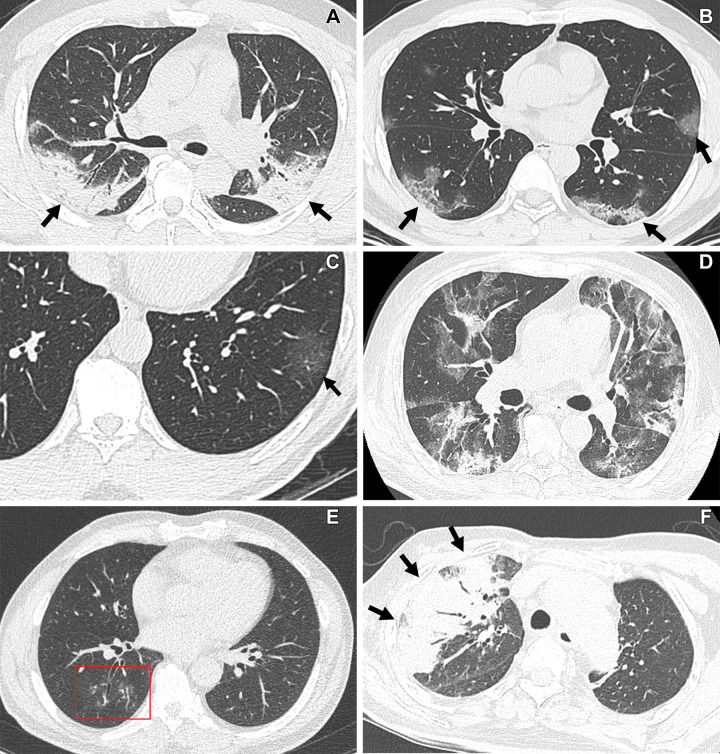
Figure 5:
CT findings of COVID-19 pneumonia according to RSNA CT classification schemes. (A, B) “Typical” COVID-19 pneumonia according to the RSNA chest CT classification system. (A) Transverse nonenhanced CT scan (lung window) obtained in a 48-year-old unvaccinated man with a history of hypertension and diabetes seen at the wild type–dominant period shows bilateral areas of consolidation with peripheral distribution (arrows). (B) Transverse nonenhanced CT scan (lung window) obtained in a 40-year-old unvaccinated man with no underlying disease seen at the wild type–dominant period shows patchy areas of mixed ground-glass opacity (GGO) and consolidation with subpleural distribution (arrows). (C, D) “Indeterminate” COVID-19 pneumonia according to the RSNA chest CT classification system. (C) Transverse nonenhanced CT scan (lung window) obtained in a 61-year-old unvaccinated woman with no underlying disease seen at the wild type–dominant period shows focal area of GGO (arrow) in left lower lobe. (D) Transverse nonenhanced CT scan (lung window) obtained in a 65-year-old fully vaccinated man with hypertension, diabetes, and a history of renal transplant seen at the Delta variant–dominant period shows extensive areas of mixed GGO and consolidation without zonal predominance. (E, F) “Atypical” COVID-19 pneumonia according to the RSNA chest CT classification system. (E) Transverse nonenhanced CT scan (lung window) obtained in a 42-year-old woman who received a booster dose with no underlying disease seen at Omicron variant–dominant period shows poorly defined small nodules (box) with peribronchial distribution in the right lower lobe. (F) Transverse nonenhanced CT scan (lung window) obtained in a 68-year-old unvaccinated man with history of cerebrovascular accident seen at Omicron variant–dominant period shows segmental area of consolidation (arrows) with air bronchogram in the right upper lobe.