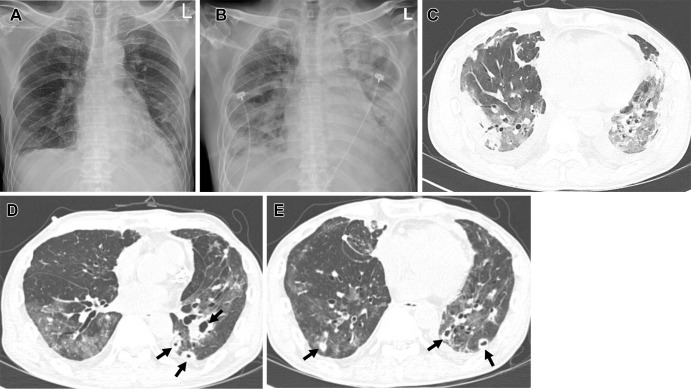
Figure 7:
COVID-19 pneumonia during an Omicron BA.5 subvariant–predominant period in a 58-year-old man with a history of lung transplant for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis who had received a booster dose of vaccine. (A) Chest radiograph obtained 7 days after positive nucleic acid amplification test for COVID-19 shows parenchymal opacity involving peripheral portion of both lower lungs. (B) Follow-up chest radiograph obtained 2 days after the initial chest radiograph demonstrates increased parenchymal opacity and extensive consolidation in the lungs. (C) Transverse nonenhanced CT scan (lung window) obtained at the level of segmental bronchi of both lower lobes 9 days after SARS-CoV-2 infection demonstrates extensive areas of mixed ground-glass opacity (GGO) and consolidation, with a peripheral predominance. (D, E) Follow-up transverse nonenhanced CT scans (lung window) obtained at levels of inferior pulmonary veins (D) and segmental bronchi of both lower lobes (E) 3 weeks after SARS-CoV-2 infection demonstrate decreased extent of GGO and consolidation, but multiple nodules (arrows) with or without cavity are scattered in bilateral lungs. Galactomannan antigen test for Aspergillus was positive at this time. The patient died with acute respiratory distress syndrome.