Figure 1.
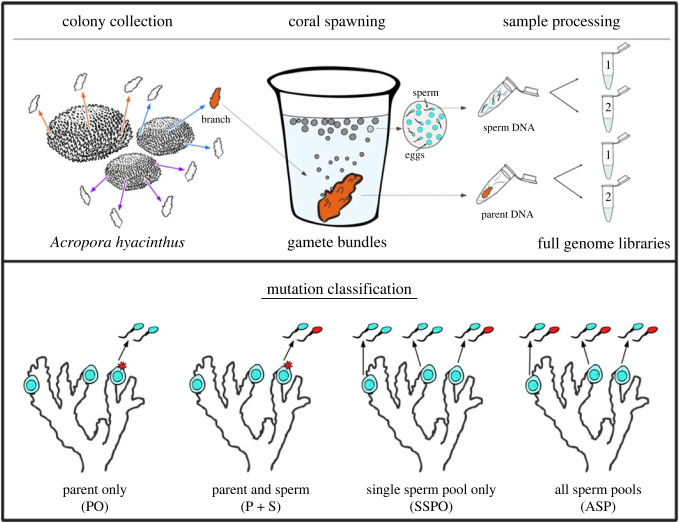
Data collection (top) and mutation classification (bottom). Top: 20 min prior to spawning, 3–4 branches were broken off of three parent colonies and placed into individual cups of seawater, for a total of 10 branches in cups. Branches then released eggs and sperm into each cup, and sperm was collected from the cup. Both the sperm pool and the parent samples were stored in RNAlater and frozen. Genomic DNA was extracted from each parent branch and sperm pool (see Methods). For each genomic DNA extraction we constructed two full genome libraries (see Methods) for technical replication. Mutation classifications (bottom, left to right): 1) a mutation unique to a single branch of the colony, but the sperm from the branch does not share the mutant genotype (parent only, PO); 2) a mutation unique to a single branch of the colony, and the sperm from the branch shares the mutant genotype (parent and sperm, P + S); 3) a mutation unique to just one sperm pool in the colony, not shared by other sperm pools or the parent branches (single sperm pool only, SSPO); and 4) a mutant genotype shared by all sperm pools from a particular colony, but none of the parent branches in that colony (all sperm pools, ASP). Figure by Shayle Matsuda.