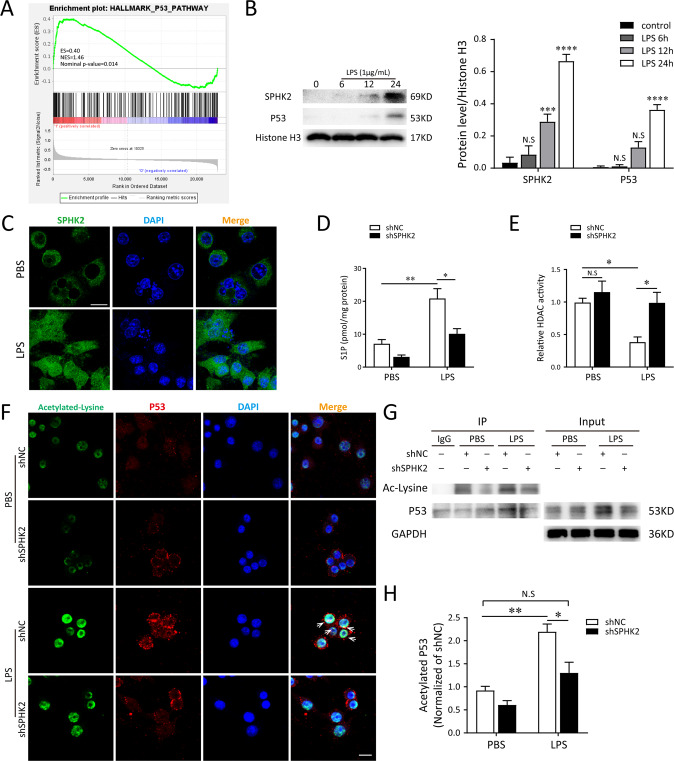
Fig. 4. The activation of nuclear SPHK2/S1P signaling promotes p53 acetylation in LPS-induced macrophages.
A Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) analysis identified the enriched gene sets in AMs exposed to saline or LPS from the same individuals (n = 7). Exposure to LPS was associated with p53 pathway. NES, normalized enrichment score. B Expressions of nuclear SPHK2 and p53 protein were detected by western blot after LPS stimulation. C Representative confocal microscopic images of SPHK2 (green) in RAW264.7 cells with or without LPS stimulations. bar = 50 μm. Gene-modified RAW264.7 macrophages were treated with 1 μg/mL LPS for 24 h. S1P levels (D) in the nuclear fraction was determined by LC-MS/MS and cell lysates were detected for HDACs activity (E) using a commercial kit. F Representative confocal microscopic images of gene-modified RAW264.7 cells co-localization with Acetylated-lysine (green) and p53 (red). bar = 25 μm. G and H Acetylation of p53 after 1 μg/mL LPS exposure was determined by Co-IP with an anti-p53 antibody, followed by western blot analysis of acetylated-lysine. Data were presented as the means ± SEM from at least 3 independent experiments. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.005; ****p < 0.001; N.S., not significant.