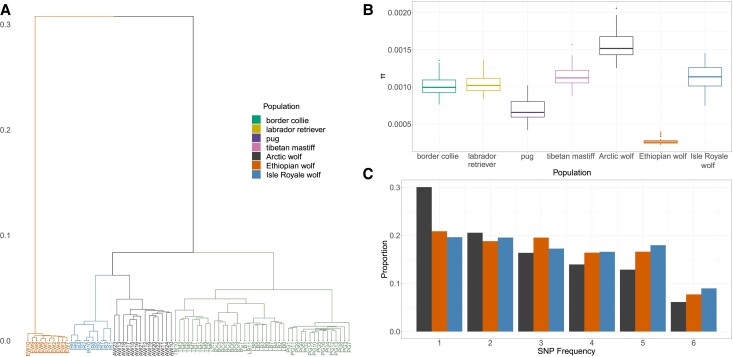
Fig. 1.
Summaries of genetic variation in the Ethiopian wolf compared with other canids. (A) Hierarchical clustering based on shared IBS loci between individuals, where the dendrogram is cut into K = 4 groups. Note that the Ethiopian wolves are an outgroup compared with other canids. (B) Diversity in dogs and wolves measured using the average number of pairwise differences between sequences, π. Ethiopian wolves have exceptionally low genetic diversity. Boxes represent the distribution over each chromosome. (C) The folded site frequency spectrum (SFS) for each wolf population. The full-unfolded SFS can be found in supplementary fig. S2, Supplementary Material online.