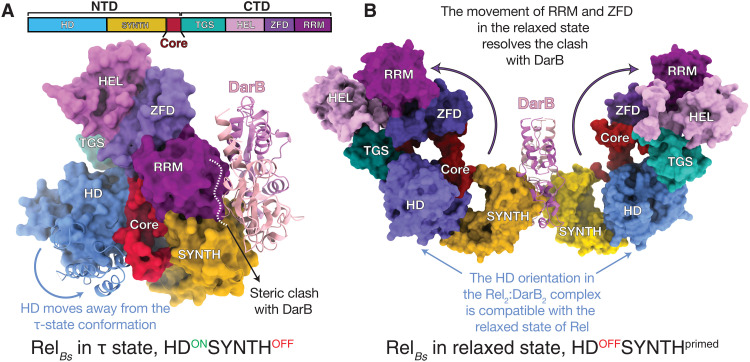
Fig. 6. DarB as a conformational selector of RelBs.
(A) Surface representation of an idealized (unrealistic) model of full-length RelBs in the hydrolase-compatible τ state superimposed on the crystal structure of the DarB:RelBsNTD complex (used only to illustrate why access to the τ state is sterically blocked). Comparison of the two structures shows that the closed HD-active τ state is not compatible with the binding of DarB due to the sterical clash of DarB with the RRM and ZFD domains and the closing of the SYNTH active site by HD. (B) Model of the full-length RelBs:DarB heterotetrameric complex in the HDOFF SYNTHprimed relaxed state. The rearrangement of RRM and ZFD domains allows for binding of DarB that, in turn, precludes the recoil of the CTD and corresponding inactivation of the HD. In both (A) and (B), Rel models were based on the structures of A. baumannii SpoT in the τ and relaxed states (10).