FIG 1.
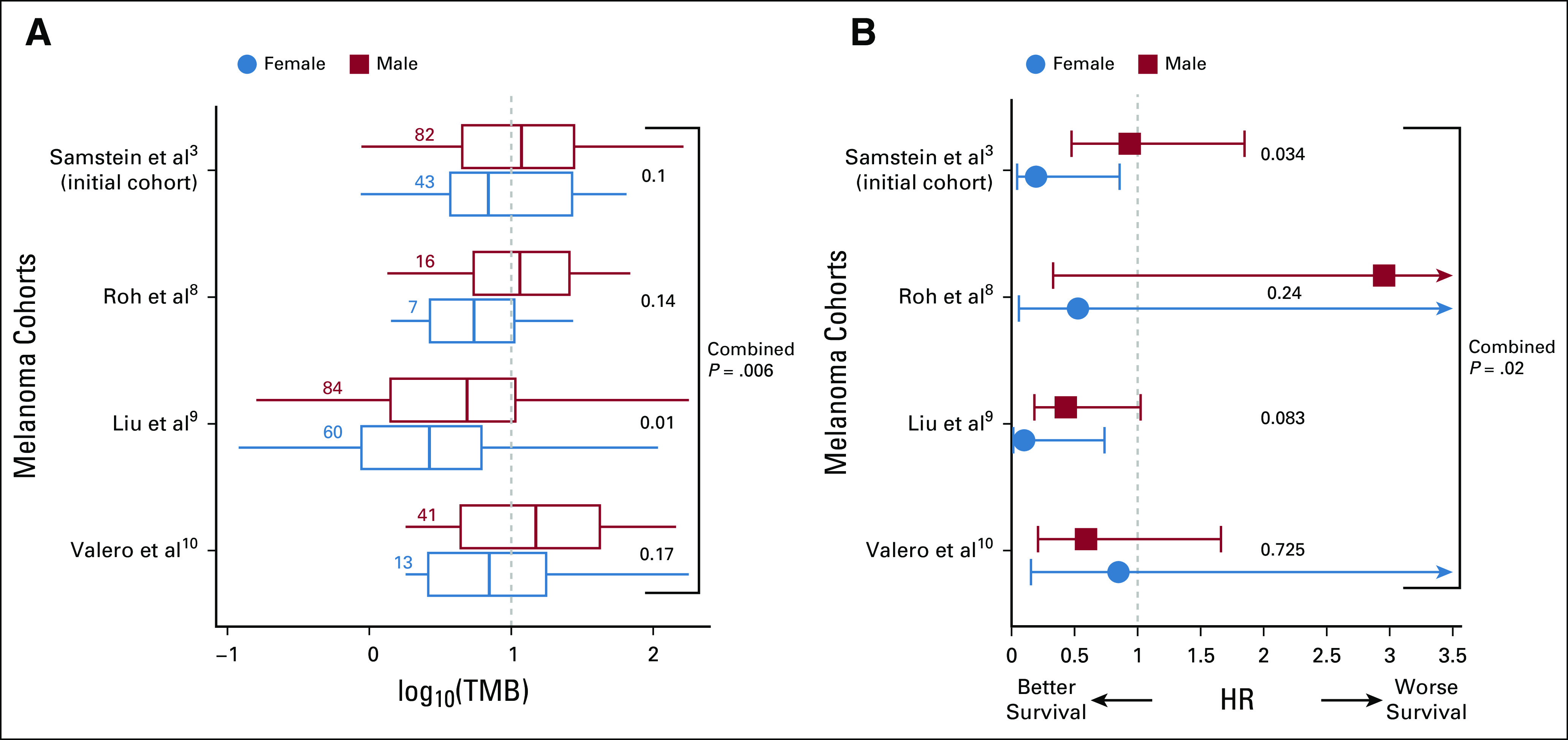
The association between high TMB status and survival of melanoma patients after anti-PD1/PDL1 treatment is dependent on the sex of the patients. (A) The distribution of log10(TMB) and the number of single nucleotide variants per megabase of sequenced genome (x-axis) for male and female patients for four different melanoma cohorts (Samstein et al,3 Roh et al,8 Liu et al,9 and Valero et al10; y-axis). The blue-dotted vertical line denotes the FDA-approved TMB threshold for pembrolizumab of 10 mut/Mb. The number of samples in each group is provided alongside the respective box plots. The center line, box edges, and whiskers denote the median, interquartile range, and the rest of the distribution in respective order, additionally showing outliers. P values of TMB differences are calculated using a one-tail Wilcoxon rank-sum test and provided on the right-hand side of each box plot. (B) HRs for male (red) and female (blue) patients with high TMB (≥ 10 mutation/Mb) versus the rest (x-axis) in four different melanoma cohorts (y-axis). Bars represent the standard 95% CIs. The significance of difference in male versus female hazard ratios is computed using a Wald test for the contribution of the coefficient of the interaction between TMB threshold and sex in a Cox proportional-hazards model. FDA, US Food and Drug Administration; HR, hazard ratio; PD1, programmed cell death protein 1; PDL1, programmed death-ligand 1; TMB, tumor mutational burden.
