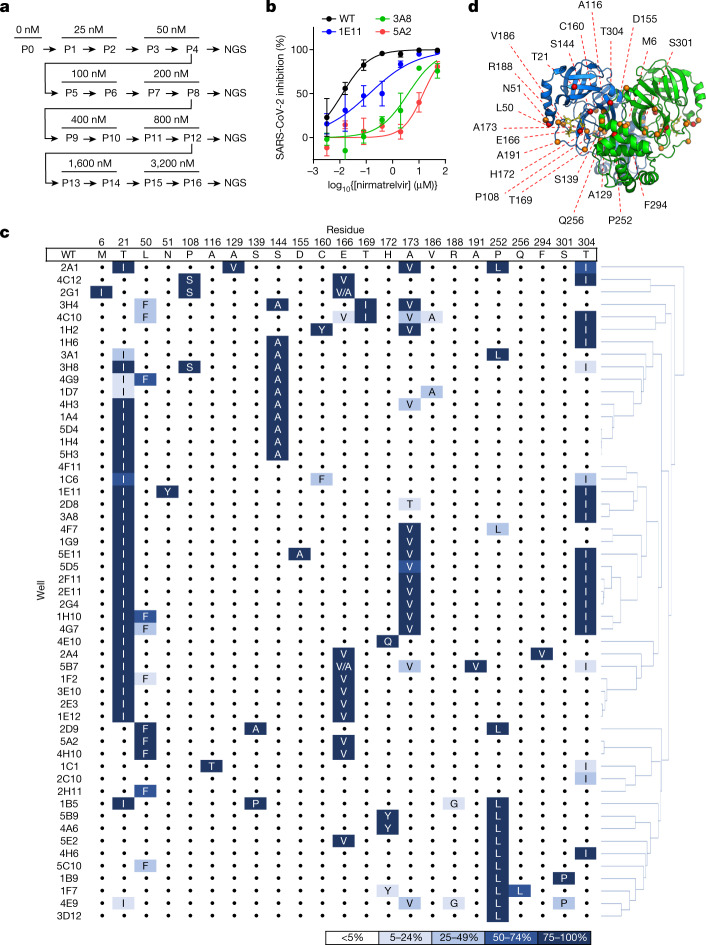
Fig. 2. Identification of nirmatrelvir resistance at scale in Huh7-ACE2 cells.
a, Passaging scheme: 480 wells were infected with SARS-CoV-2-mNeonGreen and passaged to fresh Huh7-ACE2 cells every 3–4 days, with the concentration of drug doubled every two passages. b, Validation of nirmatrelvir resistance of three wells from passage 16. These viral populations had the following mutations: 3A8 (T21I, T304I), 1E11 (T21I, N51Y, T304I) and 5A2 (L50F, E166V). See Supplementary Table 1 for exact frequencies. Representative curves from a single experiment from two biologically independent experiments are shown. Error bars denote mean ± s.e.m of three technical replicates. c, Mutations in 3CLpro found in passage 16 from 53 wells. Dots indicate WT at that residue. Mutations are shaded according to frequency. d, Residues mutated in passaging in Huh7-ACE2 cells overlaid onto the 3CLpro structure with nirmatrelvir bound. All 23 mutated residues across all resistant populations are indicated for any individual isolate having between one and six mutations. The Cα of each residue that was mutated is denoted by a red sphere for mutations observed more than ten times, and is denoted by an orange sphere for mutations observed fewer than ten times. The 3CLpro–nirmatrelvir complex was downloaded from PDB under accession code 7VH8.