Fig. 4.
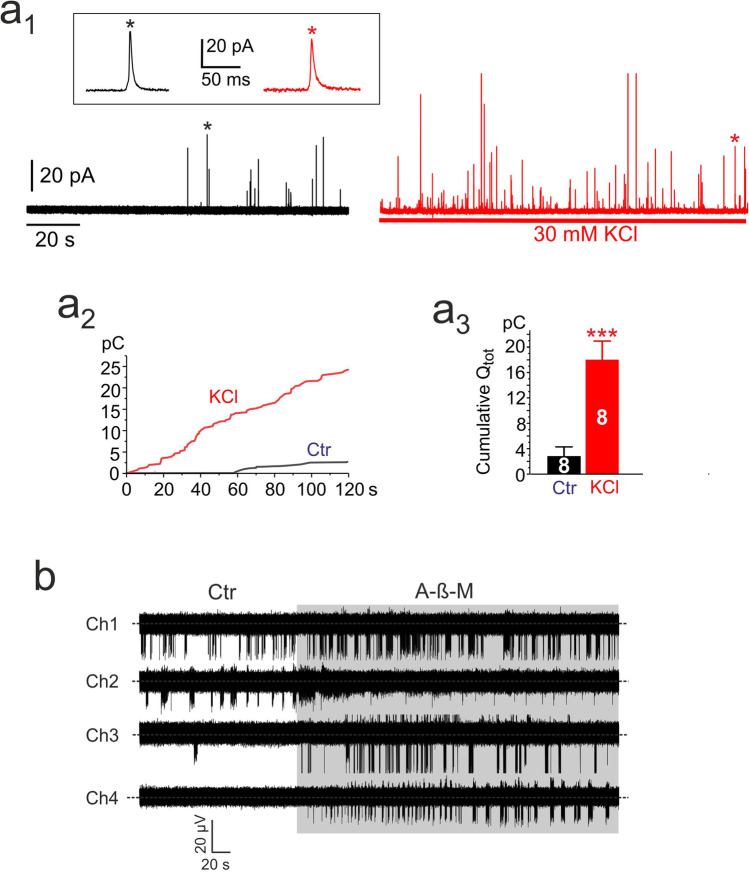
Rat CCs secrete catecholamines and respond to muscarinic agonists on MEAs. a RCCs preserve their spontaneous catecholamine (CA) secretory activity, recorded with a carbon fiber microelectrode (CFE) directly positioned on top of a CC plated on plastic dishes. a1 CA release in form of amperometric spikes is evident during resting conditions and increases markedly during addition of 30 mM KCl. Inset on top: single amperometric spikes recorded under basal (black; *) or KCl stimulation (red; *). The characteristic kinetic parameters of spikes did not change significantly during KCl stimulation (see text). a2 Overlap of cumulative secretion plots obtained from the amperometric recording of panel a1 during control (black line) and KCl application (red line). a3 Mean total cumulative charges calculated at the end of 120 s recording (Qtot) in control (black bar) and KCl application (red bar) (n = 8 cells; ***p < 0.001, paired Student’s t-test). b Rat CCs eAP firing activity of four representative MEA electrodes (Ch; channel) recorded in control conditions (white window) are compared with those recorded in the presence of methacholine (A-ß-M, 100 µM) (grey window). Notice the variable effects from cell to cell