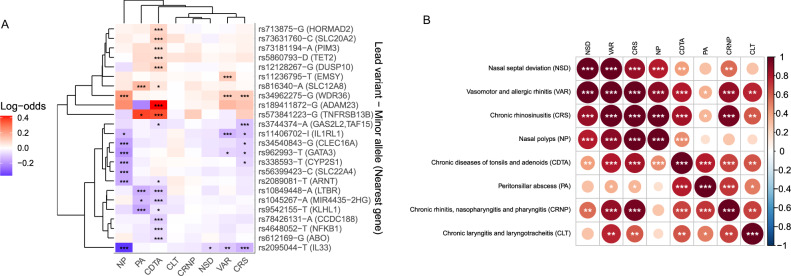
Fig. 1. Shared heritability among inflammatory and infectious upper respiratory diseases (IURDs).
A (left): effect sizes of lead variants of 24 non-HLA loci across IURD phenotypes. Red indicates a positive and blue a negative effect size estimate (in log-odds) using logistic regression (Methods). P values were calculated using upper tail chi-square testing (one degree of freedom) from a t-statistic under a normal approximation. Variants and phenotypes are ordered according to hierarchical clustering (Methods). The clusters show shared genetic heritability for variant clusters between recognized phenotype groups of sinonasal (NSD, VAR, CRS, NP) and pharyngeal diseases (CDTA, PA). *p < 0.00027, **p < 5e-8, ***p < 5e-9. B (right): genetic correlation of IURDs distinguishing vasomotor and allergic rhinitis (VAR), chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS), and nasal polyposis (NP) as a near-completely genetically correlated cluster. The color of the circle indicates genetic correlation with red indicating positive correlation and blue indicating negative correlation. P values were calculated using upper tail chi-square testing (one degree of freedom) from a z statistic. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.005, ***p < 8.4e-5.