Figure 1.
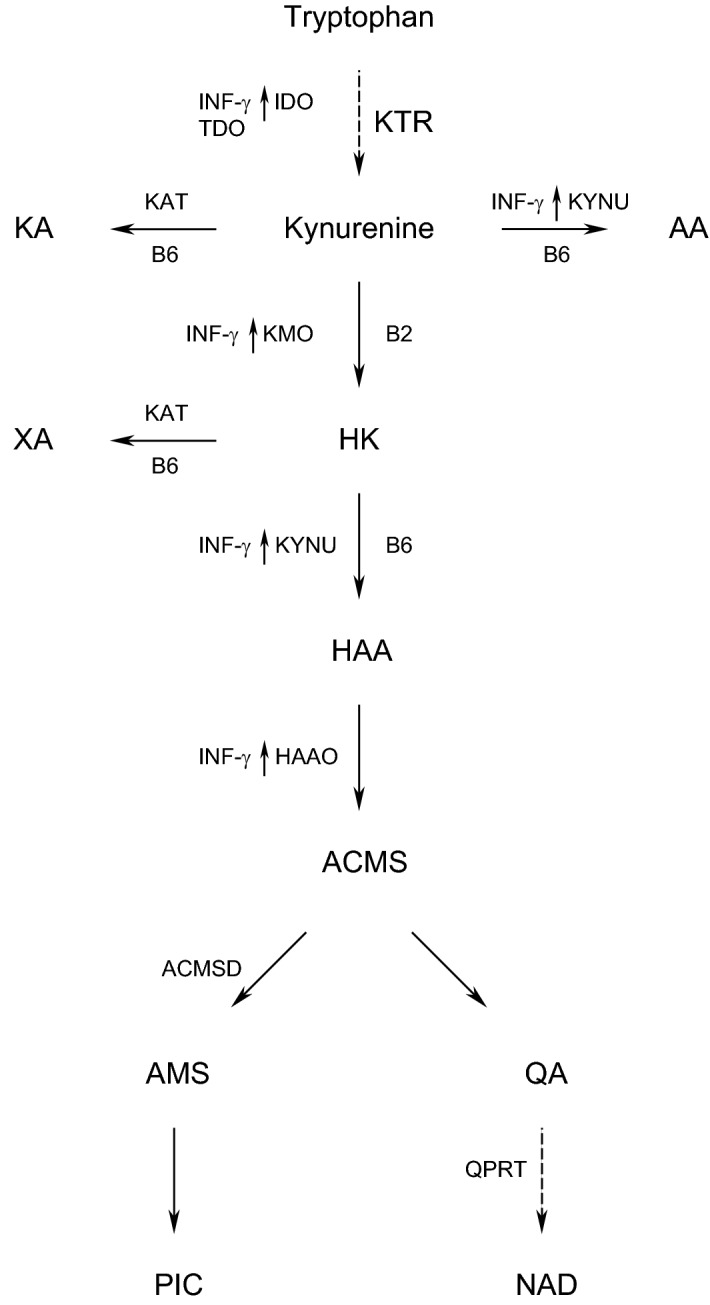
The kynurenine pathway of tryptophan metabolism, with enzymes and cofactors involved. Dashed arrow shafts indicate reactions with more than one step: Black arrows pointing up-wards indicate the enzymes which are stimulated by IFN-γ. AA: anthranilic acid; ACMS: α-amino-β-carboxymuconate-ε-semialdehyde; ACMSD: α-amino-β-carboxymuconate-ε-semialdehyde decarboxylase; AMS: α-aminomuconate-ε-semialdehyde; B2: vitamin B2 (flavin adenine dinucleotide); B6: vitamin B6 (pyridoxal 5′-phosphate, PLP); HAA: 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid; HAAO: 3-Hydroxyanthranilate 3,4-dioxygenase; HK: 3-hydroxykynurenine; IDO: indoleamine (2,3)-dioxygenase; KA: kynurenic acid; KAT: kynurenine aminotransferase; KMO: kynurenine 3-monooxygenase; KYNU: kynureninase; NAD: nicotine adenine dinucleotide; TDO: tryptophan (2,3)-dioxygenase; PIC: picolinic acid; QA: quinolinic acid; QPRT: quinolinate phosphoribosyltransferase; XA: xanthurenic acid.
