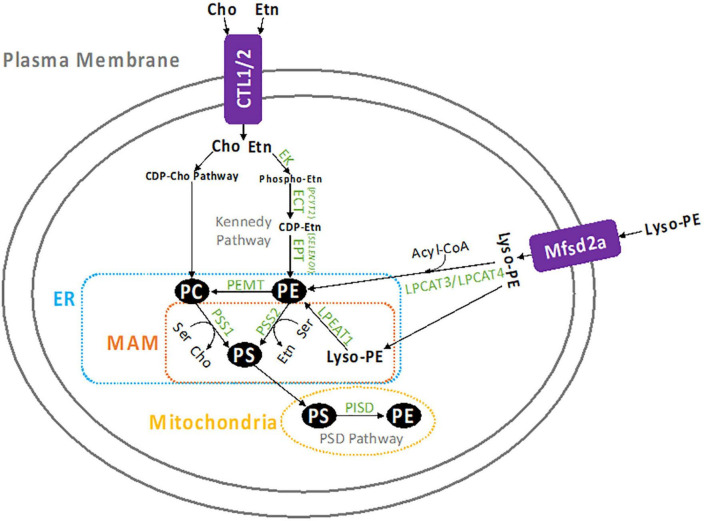
FIGURE 1.
Summary of PE metabolism. Etn enters the cell by CTL1 or CTL2, where it is converted to PE by the CDP-Etn branch of the Kennedy pathway. First Etn is converted to phosphoethanolamine and then to CDP-Etn by ECT (PCYT2), which is the rate limiting step in this pathway. CDP-Etn is converted to PE by the EPT (SELENOI). Cho is similarly used to produce PC through the CDP-Cho branch of the Kennedy pathway. Once created, PE can be converted to PC by the PEMT enzyme (mostly in the liver), or to PS by PSS2 in the MAM. The PS can be transported to the mitochondria to be decarboxylated and form PE, which is catalyzed by the PISD enzyme. Similarly, PC can be converted to PS by PSS1 in the MAM, then decarboxylated by PISD in the mitochondria to form PE. Lyso-PE can also form PE when it is transported into the cell by the Mfsd2a transporter, the acylated by LPEAT1 in the MAM, or LPCAT2, or LPCAT3 in the cytosol.