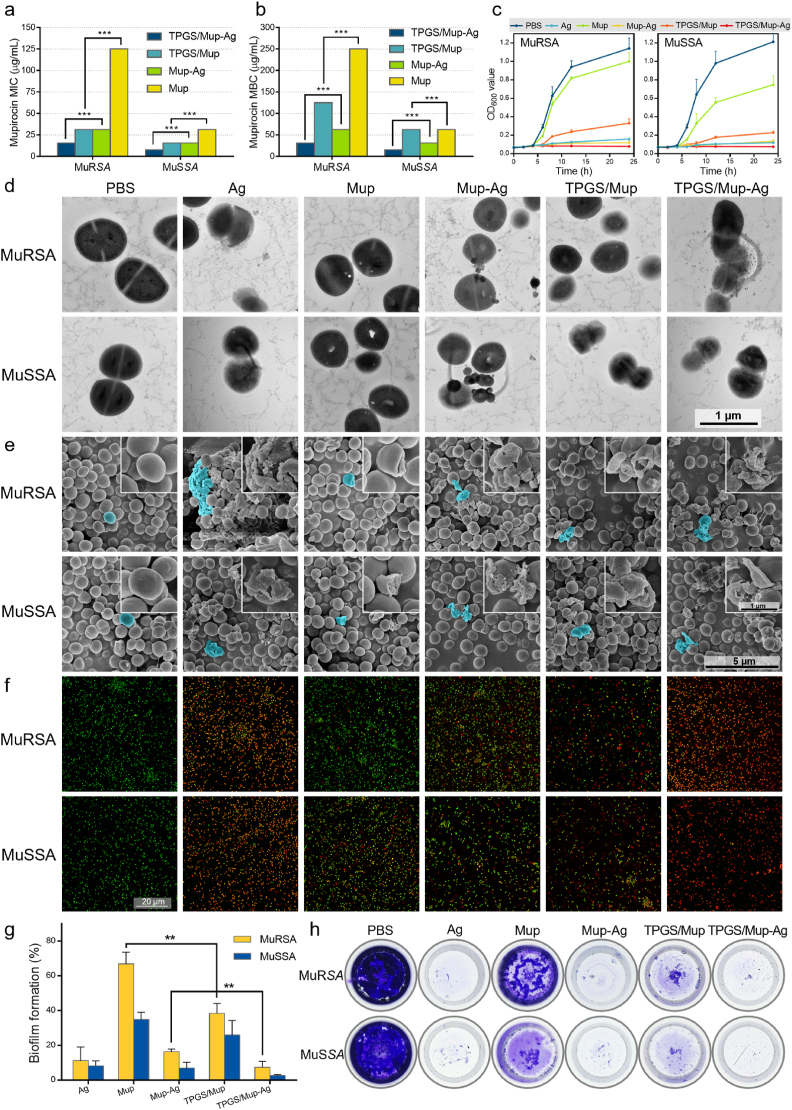
Fig. 2.
Evaluation of the antibacterial capacity of TPGS/Mup-Ag towards MuRSA and MuSSA in vitro. (A) MIC and (B) MBC susceptibility semiquantitative profiles of TPGS/Mup-Ag against MuRSA and MuSSA obtained by the microplate broth dilution method (n = 3). (C) Growth curves of MuRSA and MuSSA incubated with different preparations (n = 3). (D) Representative TEM images and (E) SEM images of MuRSA and MuSSA after incubating with different preparations for 6 h. (F) Fluorescence staining images of MuRSA and MuSSA after incubating with different preparations for 4 h. Live and dead bacteria were stained with calcein-AM (green fluorescence) and dead bacteria were stained with PI (red fluorescence). (G, H) Crystal violet staining and determination of the relative biofilm formation rate of MuRSA and MuSSA using a microplate reader upon OD590. Data are presented as the mean ± SD: ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.