Figure 2.
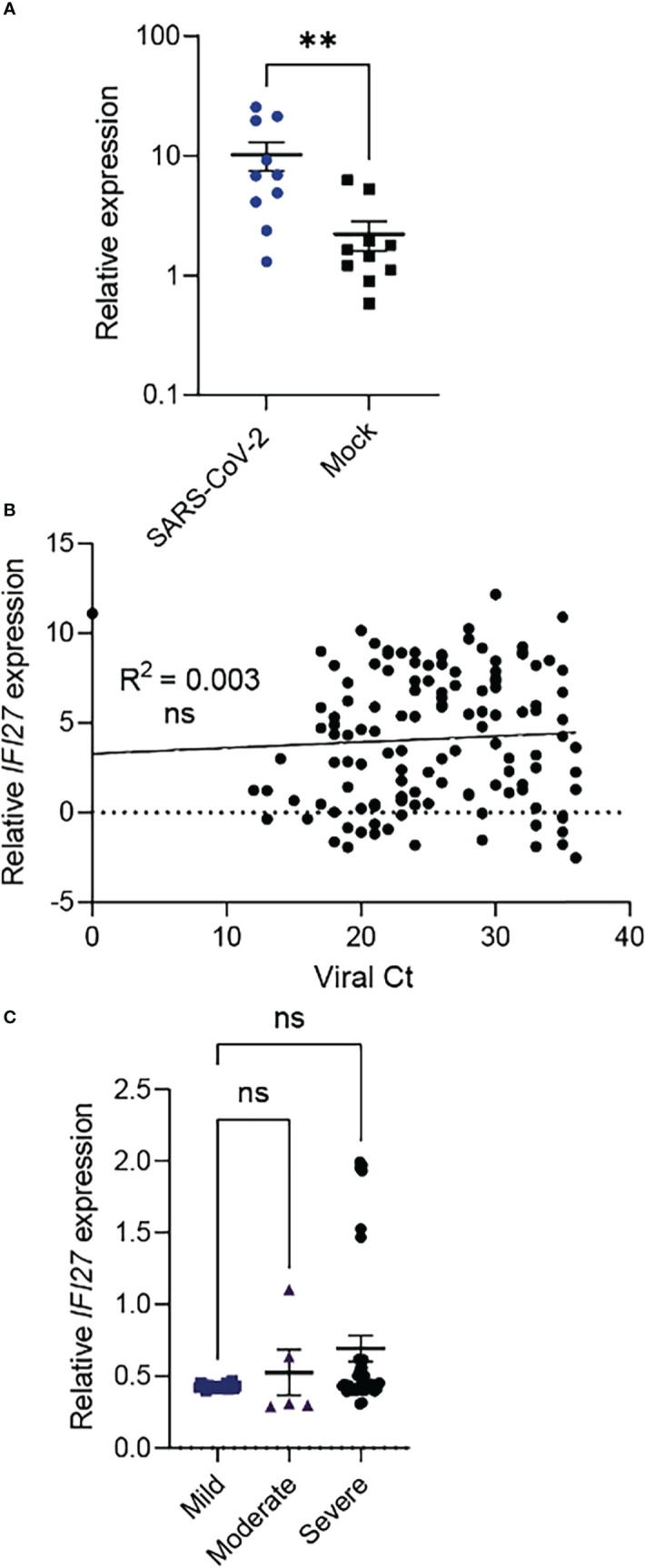
Upper respiratory tract IFI27 gene expression in COVID-19. (A) IFI27 expression in primary human nasal epithelial cells at 72 hours post-SARS-CoV-2 (QLD/02) or Mock infection. (B) IFI27 gene expression in nasopharyngeal samples in Cohort 2 (n=137). SARS-CoV-2 virus load (as measured by Ct values) is used as a proxy of local disease activity. A statistically non-significant p-value of the linear regression model (represented by R2) indicates that there is no association between IFI27 expression and viral RNA in the upper respiratory tract. (C) IFI27 gene expression in nasopharyngeal samples in Cohort 3 (n=60). ‘Mild’ disease is defined as the presence of COVID-19 disease in a patient who does not require hospitalization. ‘Moderate’ disease is defined as the presence of COVID-19 disease in a patient who requires hospitalization. ‘Severe’ disease is defined as the presence of COVID-19 disease in a patient who requires mechanical ventilation in an intensive care unit. p value is calculated using Mann-Whitney U test. **p < 0.01; ns, not significant. Data shows mean ± SEM. IFI27 gene expression is measured by qPCR normalized to house-keeping genes.
