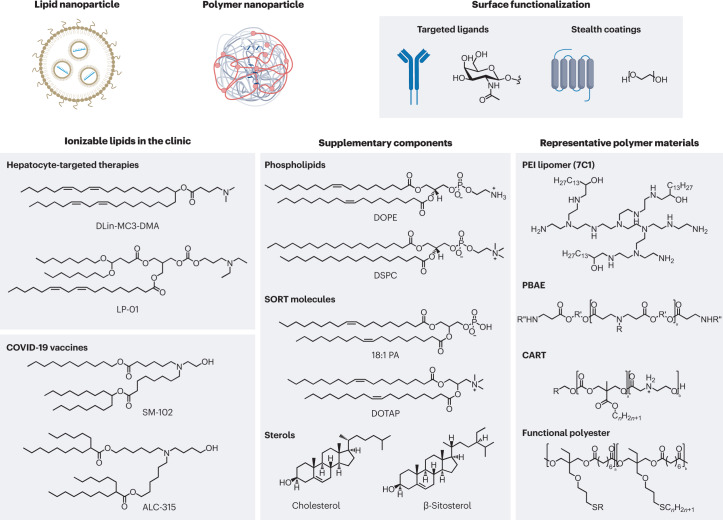
Fig. 1. Self-assembled nanoparticles based on lipid and polymer materials are the state of the art for the delivery of genetic drugs.
Currently, lipid nanoparticles that incorporate an ionizable lipid are the most advanced delivery system for genetic drugs in the clinic. These materials feature a tertiary amine that can acquire charge at acidic pH to facilitate nucleic acid loading during formulation and promote endosomal escape following cellular uptake. Dilinoleylmethyl-4-dimethylaminobutyrate (DLin-MC3-DMA) is a component of the US Food and Drug Administration-approved drug Onpattro. LP-01 is a component of Intellia Therapeutics’ clinical candidates NTLA-2001 and NTLA-2002 for gene editing in the liver, and SM-102 and ALC-315 are the ionizable lipid components of the Moderna and Pfizer–BioNTech vaccines, respectively. Alternatively, certain polymers that incorporate ionizable amine groups can also be used to formulate nanoparticles, and the choice of monomers will impact nanoparticle delivery efficiency and tissue selectivity. For both ionizable lipids and polymers, supplementary components can be included to improve the stability, fusogenicity (the ability to facilitate fusion with cellular membranes) and selectivity of the formulated nanoparticle. Additionally, the surfaces of these nanoparticles can be further modified using synthetic or biological targeting ligands and stealth coatings to alter nanoparticle circulation time, biodistribution and cellular uptake. Nucleic acid biomolecules can be loaded into nanoparticles to reprogramme the central dogma of biology through gene silencing, expression and editing to correct the course of disease. 18:1 PA, 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphatidic acid; CART, charge-altering releasable transporter; DOPE, 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine; DOTAP, 1,2-dioleoyl-3-trimethylammonium-propane; DSPC, 1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine; PBAE, poly(beta-amino ester); PEI, polyethyleneimine; SORT, selective organ targeting.