Figure 2. Hypoxia enhances neutrophil binding on E-selectin and neutrophil-platelet aggregation.
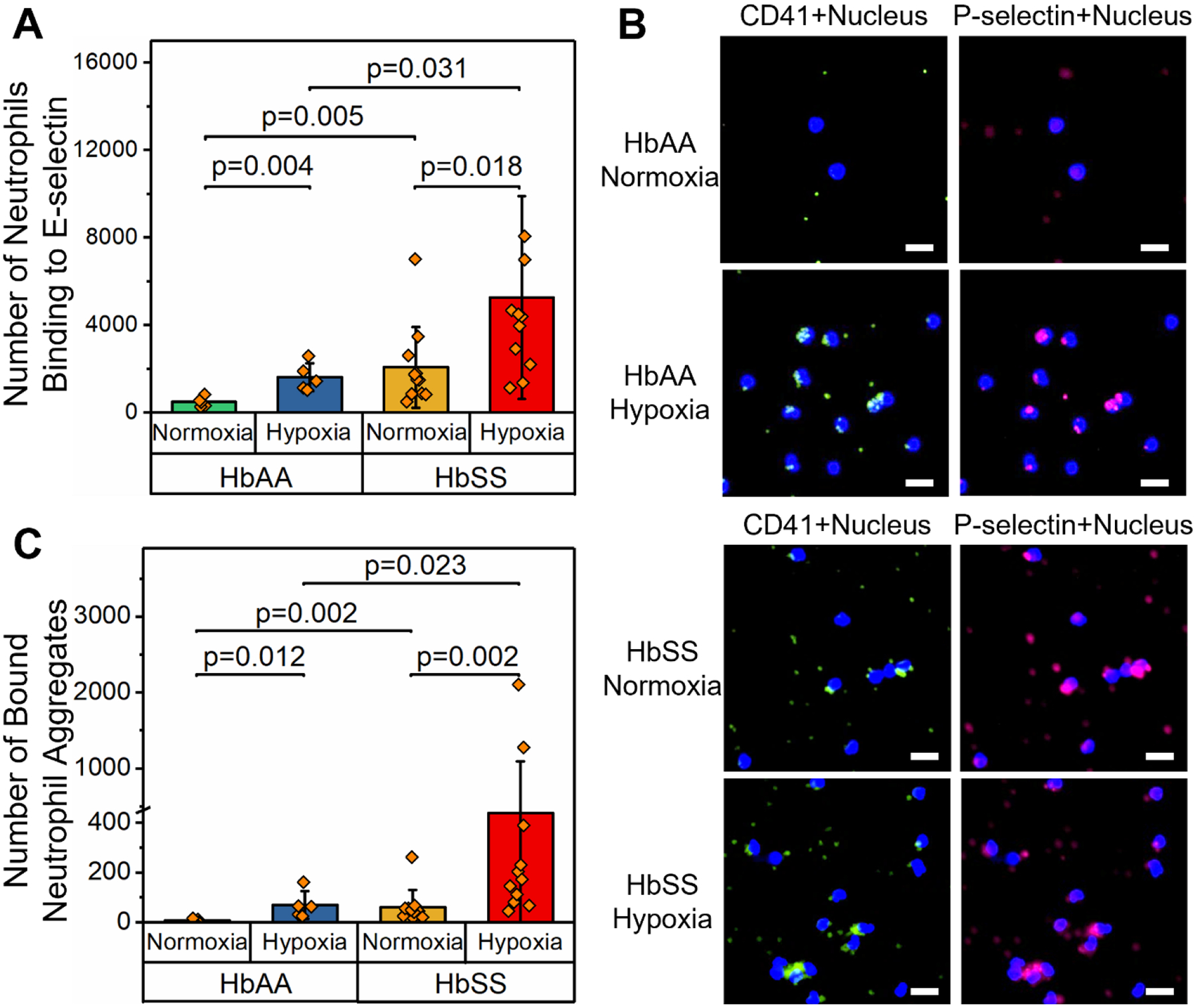
(A) The number of neutrophils binding to E-selectin was significantly greater under hypoxic conditions compared to normoxia in both HbAA (N = 5, P = 0.004, paired t-test) and HbSS (N = 11, P = 0.018, Mann-Whitney) clinical samples. Further, the number of neutrophils binding to E-selectin was significantly greater in samples from subjects with HbSS than HbAA under both normoxia (P = 0.005, Mann-Whitney) and hypoxia (P = 0.031, Mann-Whitney). (B) Representative fluorescent microscopic images showing adherent neutrophil aggregates bridged by platelets in samples from subjects with HbAA or HbSS, under hypoxic or normoxic conditions. Neutrophils were stained with DAPI, platelets were stained with FITC-conjugated anti-CD41 and Cy5-conjugated anti-P-selectin antibodies. Scale: 20 μm. (C) The number of bound neutrophil aggregates was significantly greater under hypoxia than normoxia in samples from subjects with HbAA (N = 5, P = 0.012, Mann-Whitney) and HbSS (N = 11, P = 0.002, Mann-Whitney). Further, the number of bound neutrophil aggregates was significantly greater in samples from subjects with HbSS than HbAA under both normoxia (P = 0.002, Mann-Whitney) and hypoxia (P = 0.023, Mann-Whitney). HbAA: healthy, and HbSS: homozygous SCD.
