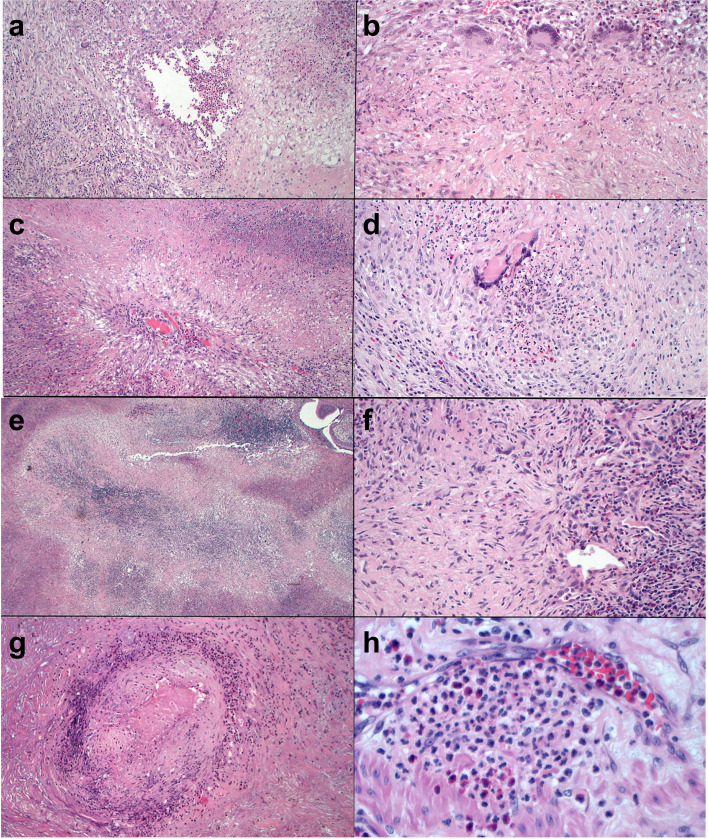
Fig. 4.
Granulomas and vasculitis in surgical lung biopsies from patient 1 (a-d) and patient 22 (e-h) of Table 1: a) This necrotizing granuloma has a central area with eosinophilic inflammation surrounded by chronic inflammation with multinucleated giant cells (hematoxylin-eosin [H&E], × 10). b) Multinucleated giant cells and lympho-plasmocytic cells surround a fibro-histiocytic central area with focal necrosis (H&E, × 20). c) This granuloma consists of a cartwheel-shaped arrangement of palisading histiocytes surrounding a central arteriole in a necrotic background (H&E, × 10). d) A granuloma with central acute inflammation (H&E, × 20). e) Large zones of basophilic necrosis with an irregular border give the appearance of geographic necrosis (H&E, × 4). f) Nodular scar with central multinucleated giant cells and adjacent vasculitis (H&E, × 20). g) Necrotizing arteritis. The wall of this arteriole shows marked inflammation and central fibrinoid necrosis (H&E, × 10). h) Neutrophilic capillaritis: the inflammation infiltrates the capillary wall with spilling over into the hematic space (H&E, × 40)