Figure 2. Fitness consequences of interspecies recombination conferring β-lactam resistance.
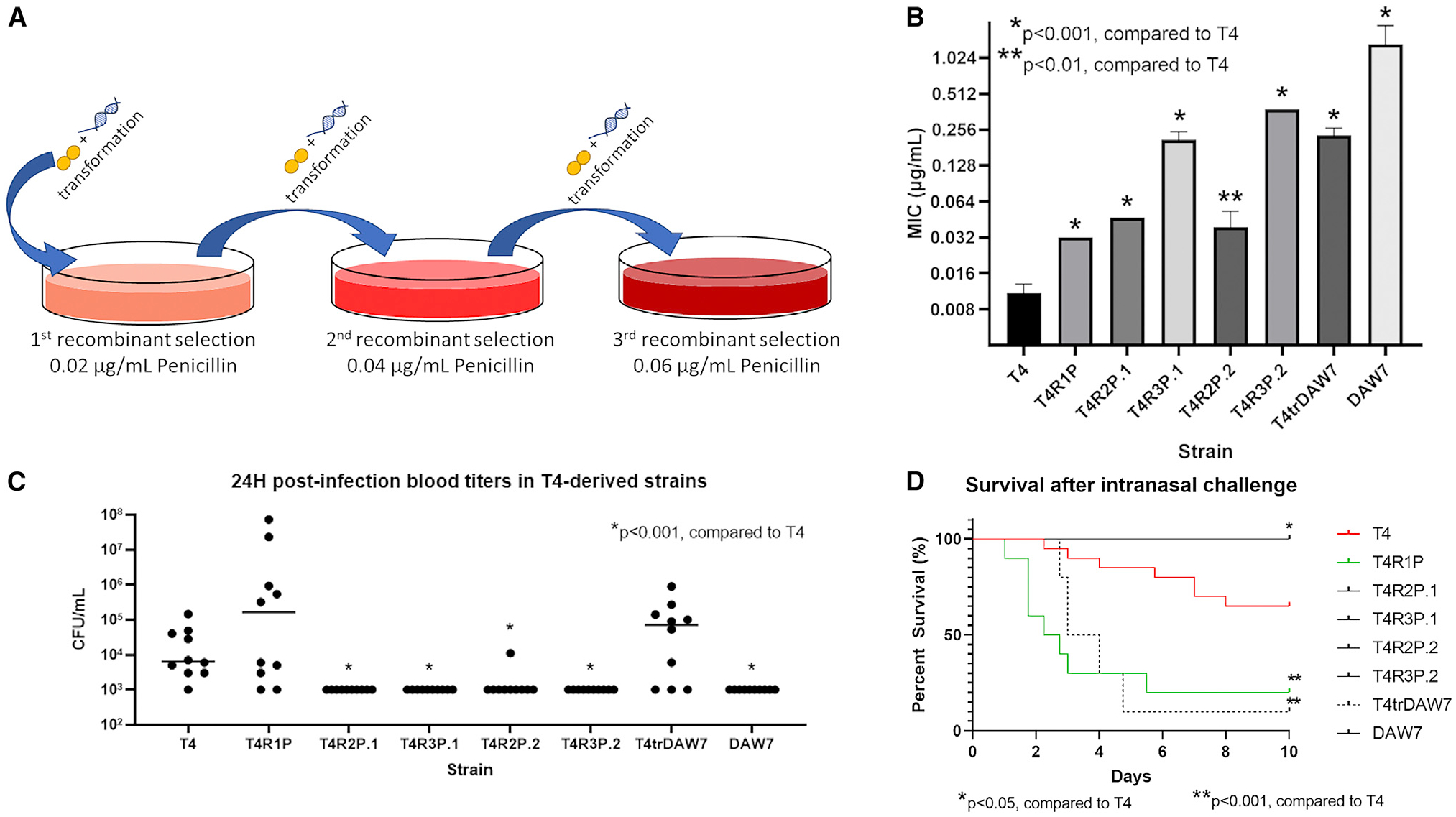
(A) Penicillin resistance was developed via serial transformation of T4 cells with 5 μg gDNA from either penicillin-resistant VGS strains or the pneumococcal strain DAW7. Colonies were screened on penicillin-containing blood agar plates and used for subsequent re-transformation with gDNA.
(B) Penicillin MICs of WT pneumococcal strain T4 and its derivative recombinant pneumococcal populations. Data are represented as mean MIC ± SD.
(C) Blood titers at 24 h post-infection.
(D) Mouse survival after intranasal challenge with recombinant versus WT. Seven-week-old BALB/c mice were intranasally infected with 106 CFUs of T4 or recombinant strains and followed for 10 days (n = 10 mice/group). p values of 0.05 or less as determined by Mann-Whitney U test were considered significant.
