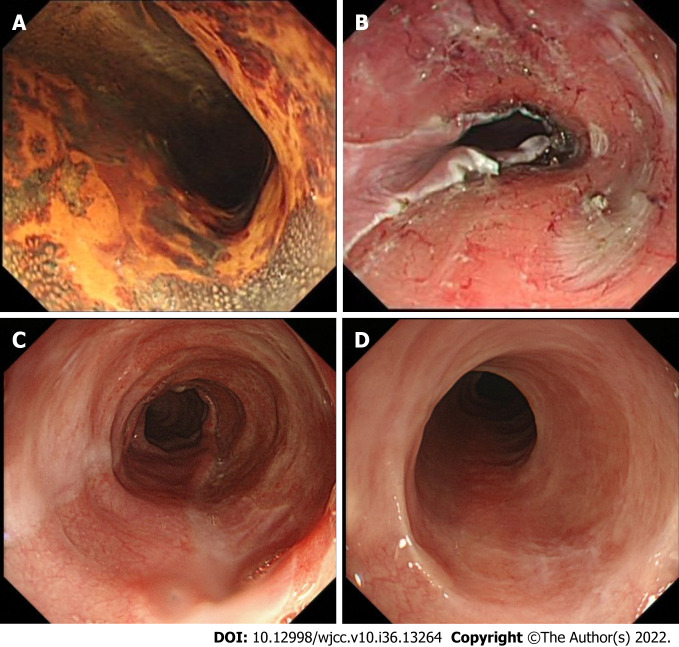
Figure 1.
Representative case (case 1). A 67-yr-old female who underwent endoscopic resection for large superficial esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. A: Endoscopic view of the tumor after Lugol’s staining. The tumor spread to more than 3/4 of the circumference of the esophageal lumen; B: Endoscopic view of the ulcer bed immediately after endoscopic submucosal dissection. The width of the mucosal defect was ≥ 3/4 and less than the entire circumference. Then oral steroid was administered as a prophylactic treatment; C: Endoscopic view on the 30th d. The mucosal defect was still undergoing re-epithelialization, and a 9.9 mm diameter gastroscope (Olympus GIF-Q260J) could pass. D: Endoscopic view on the 180th d; Complete epithelialization is shown and a 9.9 mm diameter gastroscope (Olympus GIF-Q260J) could pass without dysphagia.