Figure 2.
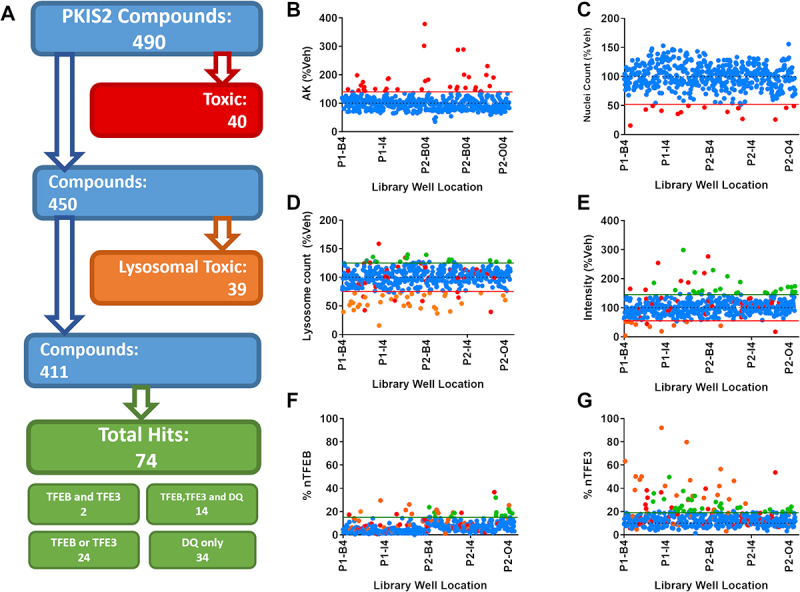
Screening the PKIS2 library. (A) The 490 PKIS2 compounds were screened at 1 µM across all assays and passed through an analysis cascade to identify nontoxic compounds which translocate TFEB and/or TFE3. (B) AK release and (C) nuclear count from immunocytochemistry images are used to assess cellular toxicity, indicated by those compounds (in red) which fall outside the 2 s.d. range of the vehicle controls (indicated by the red line). (D) Active lysosome count and (E) corrected fluorescence intensity as measured from the DQ Red BSA assay are used to assess lysosomal toxicity, indicated by those compounds (in Orange) which fall below the 2 s.d. range of the vehicle controls (indicated by the Orange line). Any which fall above the 2 s.d. range of the assay are classified as positive hits for DQ Red BSA. Remaining compounds with no associated toxicity which show nuclear translocation above the 3 s.d. range of the vehicle-only control for (F) nuclear TFEB (% nTFEB) and/or (G) nuclear TFE3 (% nTFE3) translocation are classified as positive hits. A total of 74 positive hits were identified. n = 1.
