Figure 3.
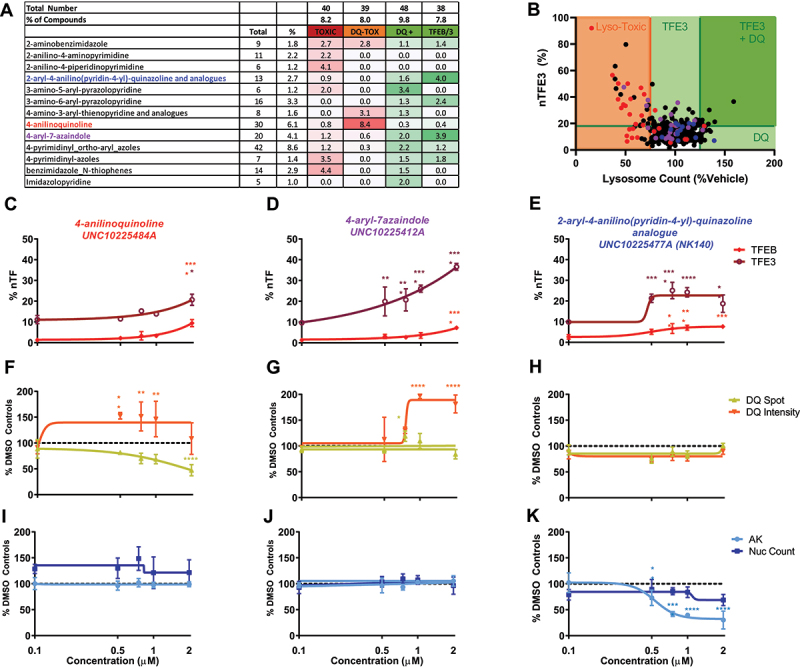
Patterns of activity enriched within identified chemotypes. (A) Chemotypes showing enrichment >2 against a particular biological output. The “2-aryl-4-anilino(pyridine-4-yl)-quinazoline and analogs” chemotype (blue) is enriched for TFEB and TFE3 translocation hits, “4-anilinoquinoline” chemotype (red) is enriched for lysosomal toxicity and the “4-aryl-azaindole” chemotype (purple) is enriched for both TFEB and TFE3 translocation and increased lysosome activity. (B) Correlation between %nTFE3 translocation and lysosome function is often associated with reduced lysosome function indicated by reduced lysosome count, particularly noticeable in the “4-anilinoquinoline” chemotype (red). (C-E) % nTF indicates the nuclear TFEB and TFE3 translocation, (F-H) DQ Red BSA degradation and (I-K) AK and nuclear count for toxicity were measured after SH-SY5Y cells were exposed to increasing concentrations of compound for 24 h (n = 1 due to compound availability; error bars = s.d.). (C, F, I) The compound UNC10225484A of the “4-anilinoquinoline chemotype” shows a modest TFEB and 3 translocation at 2 µM but a correlated drop in DQ Red BSA spot count with no indication of cellular toxicity. (D, G, J) The compound UNC10225412A of the “4-aryl-azaindole” chemotype shows strong TFE3 translocation and an increase in DQ Red BSA intensity with no toxicity. (E, H, K) The compound UNC10225477A of the “2-aryl-4-anilino(pyridine-4-yl)-quinazoline and analogs” chemotype shows modest TFEB and TFE3 translocation with no increases in DQ Red BSA intensity or cellular toxicity. AK is reduced, suggesting either decreased cell death or off-target inhibition of AK enzyme. n = 1 for all above assays, mean ±s.d. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001 Two-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test.
