Figure 1.
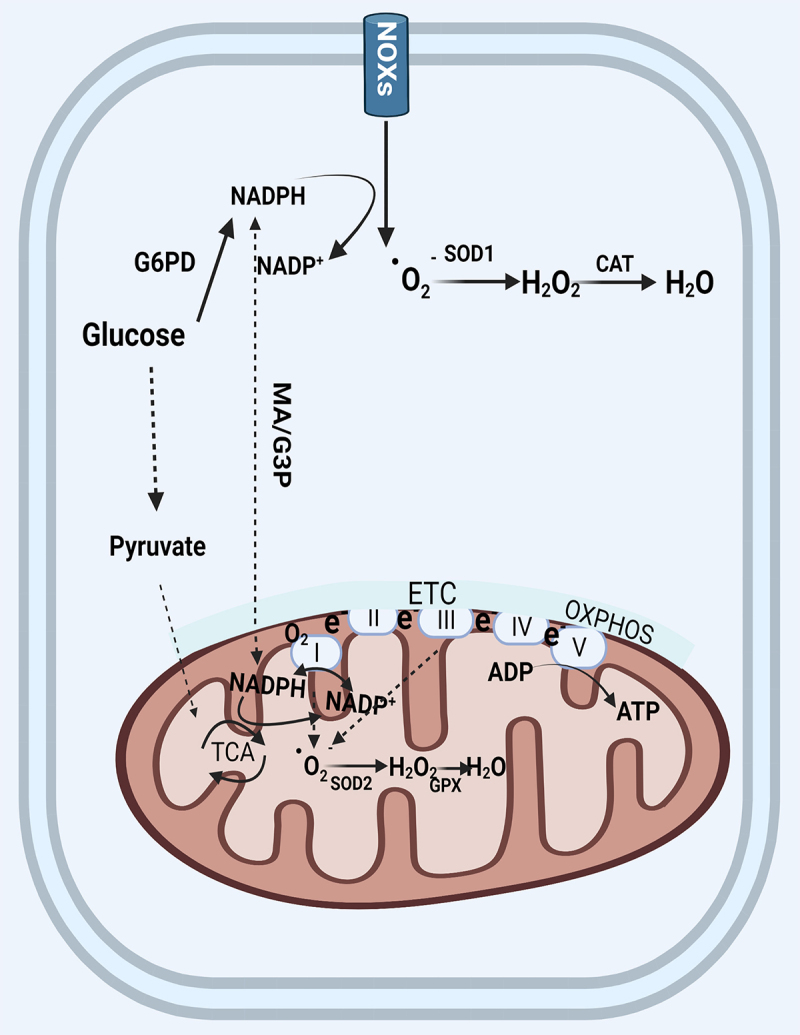
The generation and elimination of mitochondria ROS. In the cytosol, NADPH is primarily produced by G6PD in the glycolysis pathway. The cytosolic and mitochondrial NADPH is exchanged through two shuttles. NOXs transports electrons to oxygen from NADPH to produce superoxide free radical which was converted by SOD (SOD2 in mitochondria) to hydrogen peroxide, and finally converted by catalase to harmless H2O. Mitochondrial ROS are produced from the leakage of electrons to form superoxide at complex I and complex III in the electron transport chain. Mitochondria utilize oxygen to generate ATP through OXPHOS. Abbreviations: ATP: adenosine triphosphate; CAT: catalase; ETC: electron transport chain; G6PD: glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase; MA/G3P: the malate-aspartate (MA) and the glycerol-3-phosphate(G3P) shuttle; NOX: NADPH oxidase; OXPHOS: oxidative phosphorylation; SOD: superoxide dismutase; TCA: tricarboxylic acid.
