Figure 1.
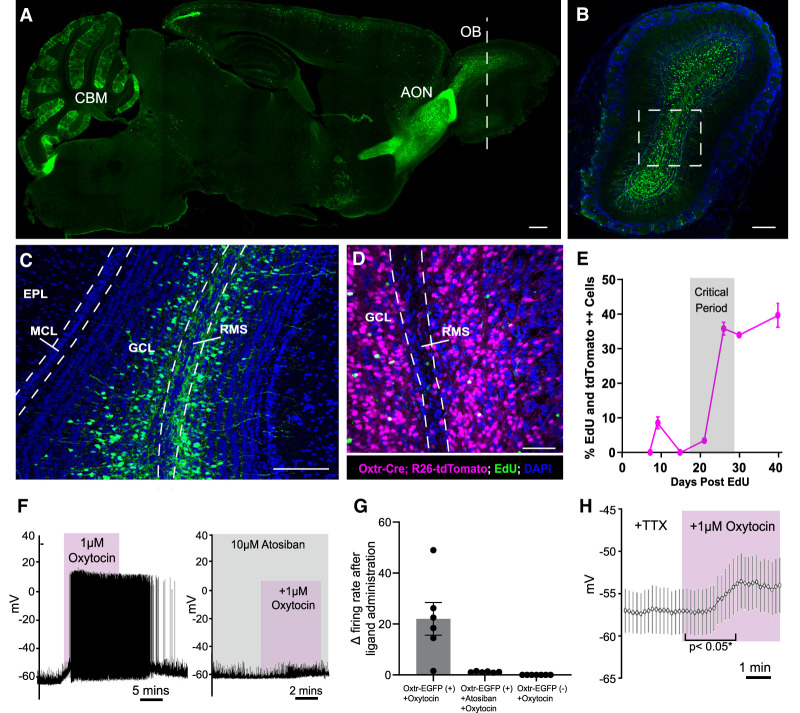
Oxytocin receptor is dynamically expressed in developing adult-born neurons, and oxytocin selectively depolarizes Oxtr+ abGCs. (A) Sagittal section of an entire mouse brain, revealing Oxtr expression using the Oxtr-EGFP reporter allele. (OB) Oflactory bulb, (AON) anterior olfactory nucleus, (CBM) cerebellum. Scale bar, 200 µm. (B) Coronal OB section of the Oxtr-EGFP reporter allele in the plane denoted by the white dashed line in A. Scale bar, 200 µm. (C) Magnified view of the white box in B. (GCL) Granule cell layer, (EPL) external plexiform layer, (MCL) mitral cell layer, (RMS) rostral migratory stream. Scale bar, 200 µm. (D) Coronal view of the Oxtr-Cre;Rosa26-tdTomato reporter allele injected with EdU. (GCL) Granule cell layer, (RMS) rostral migratory stream. Scale bar, 200 µm. (E) Quantification of EdU and Oxtr-Cre;Rosa26-tdTomato-double-positive abGCs over the course of developmental time. n = 4 animals per time point. (F, left) Representative current clamp recording from Oxtr-EGFP+ abGCs. Oxytocin (1 µM) was washed into the bath. (Right) Representative current clamp recording from Oxtr-EGFP+ abGCs. Atosiban (10 µM) was washed into the bath 5 min before oxytocin application. (G) Quantification of the change in frequency after administration of oxytocin or oxytocin + atosiban in Oxtr-EGFP+ and Oxtr-EGFP− abGCs. n = 6–8 cells from three animals. (H) Representative current clamp recording from Oxtr-EGFP+ abGCs. Oxytocin (1 µM) and TTX were washed into the bath. (*) P < 0.05, Student's t test. n = 20 EGFP+ cells from four animals. See also Supplemental Figure S1.