Figure 11.
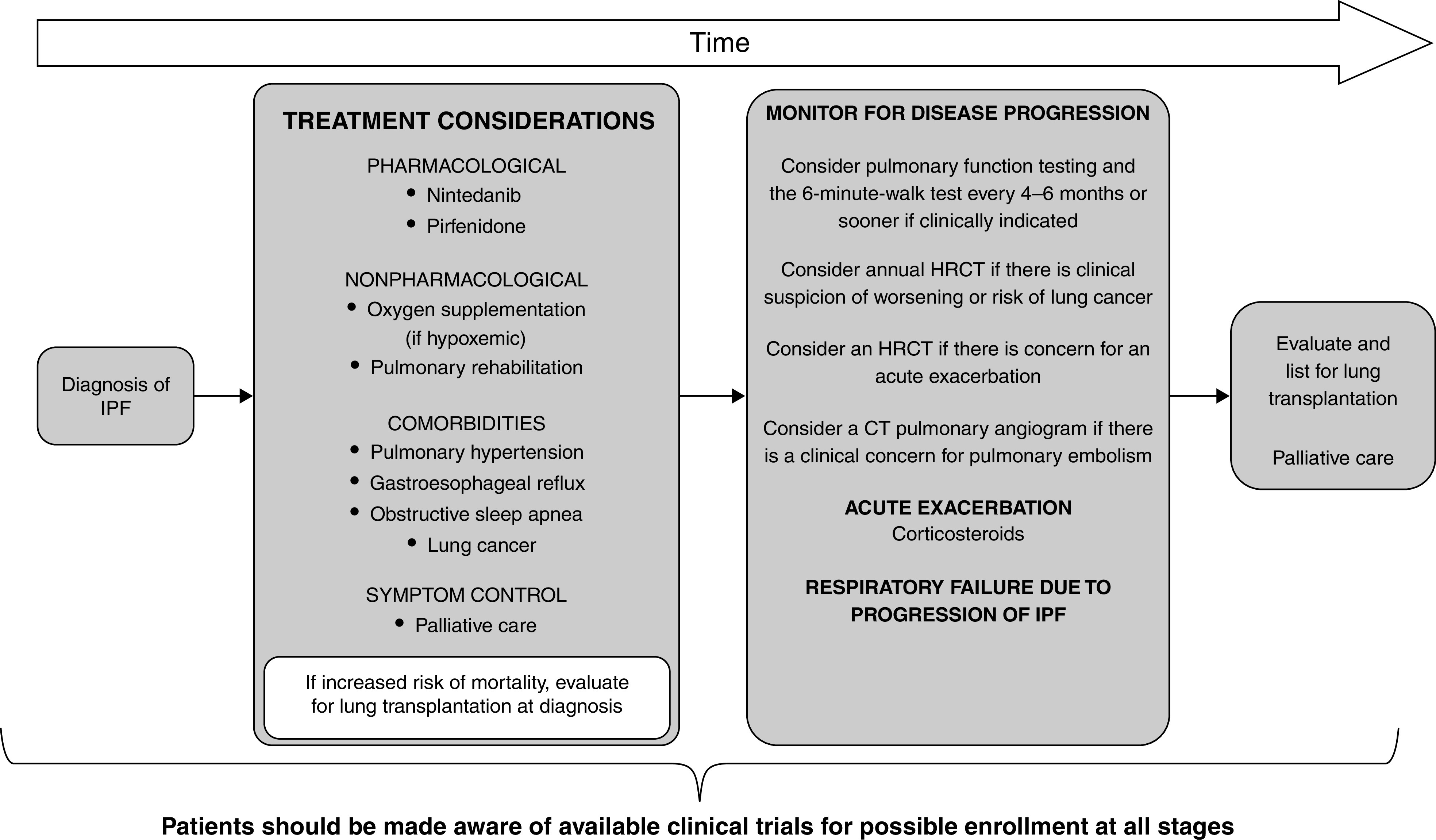
Schematic pathway for clinical management of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), developed using consensus by discussion. Treatment considerations should include both pharmacological (nintedanib and pirfenidone) and nonpharmacological (oxygen supplementation and/or pulmonary rehabilitation) therapies. Patients should be evaluated and treated for existing comorbidities, including pulmonary hypertension, gastroesophageal reflux, obstructive sleep apnea, and lung cancer. Patients may benefit from involvement of palliative care to help with symptom management (cough, dyspnea, and/or anxiety). Patient values and preferences should be explored. Patients at increased risk of mortality should be referred for lung transplantation at diagnosis. Patients should be evaluated every 3–6 months or more often for disease progression. Acute exacerbations may be treated with corticosteroids. Mechanical ventilation is not recommended for the majority of patients with respiratory failure. Adapted from Reference 1. CT = computed tomography; HRCT = high-resolution computed tomography.
