Figure 12.
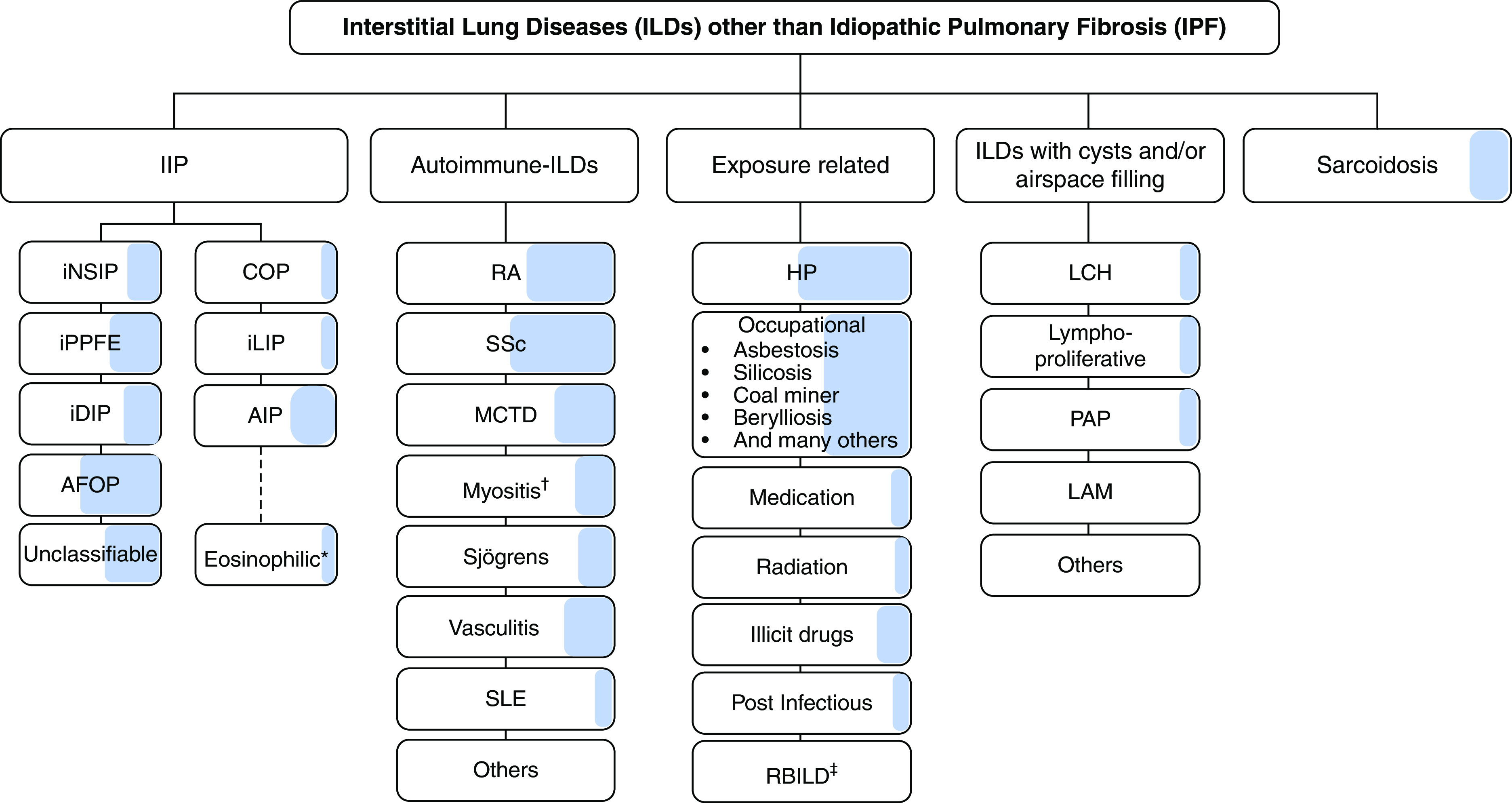
Interstitial lung diseases (ILDs) manifesting progressive pulmonary fibrosis (PPF), developed using consensus by discussion. The shaded area represents the estimated proportion of patients with various types of ILD who manifest PPF. Note that idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is not included in the figure, because it is excluded from the definition of PPF. While virtually all patients with IPF will manifest disease progression similar to PPF, the proportion of patients with ILDs other than IPF who manifest PPF is based on the consensus of opinions and the perception of the international committee. There are no data to provide the exact or estimated proportion of patients manifesting PPF in ILDs, other than IPF. *The committee acknowledges that eosinophilic pneumonia of unknown cause was not included in the IIP classification. †Myositis includes PM/DM/antisynthetase syndrome, which may be amyopathic. ‡Although respiratory bronchiolitis interstitial lung disease (RBILD) is acknowledged to be a consequence of exposure to cigarette smoke in virtually all patients with RBILD, RBILD and desquamative interstitial pneumonia (DIP) often coexist. Although DIP is also related to exposure to cigarette smoke in a majority of patients, DIP is also seen in some patients with connective tissue disease, without exposure to cigarette smoke, and without a known cause. Antifibrotic treatment is indicated for patients diagnosed with IPF (3). Antifibrotic treatment of the other types of ILD upon manifesting PPF is as suggested/recommended in this guideline. AFOP = acute fibrinous and organizing pneumonia; AIP = acute interstitial pneumonia; COP = cryptogenic organizing pneumonia; DM = dermatomyositis; HP = hypersensitivity pneumonitis; iDIP = idiopathic DIP; IIP = idiopathic interstitial pneumonia; iLIP = idiopathic lymphoid interstitial pneumonia; iNSIP = idiopathic nonspecific interstitial pneumonia; iPPFE = idiopathic pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis; LAM = lymphangioleiomyomatosis; LCH = Langerhans cell histiocytosis; MCTD = mixed connective tissue disease; PAP = pulmonary alveolar proteinosis; PM = polymyositis; RA = rheumatoid arthritis; SLE = systemic lupus erythematosus; SSc = systemic sclerosis.
