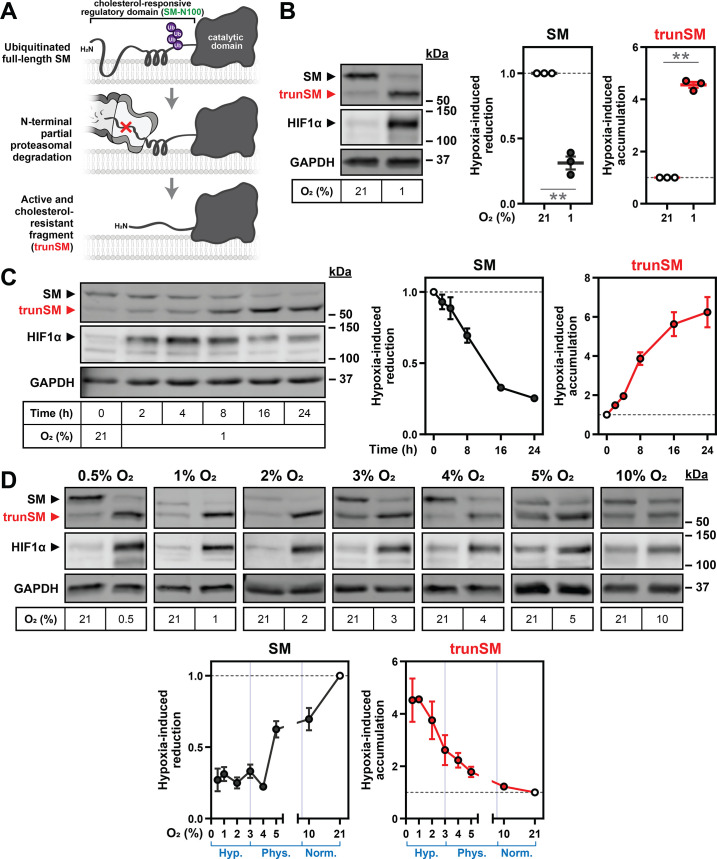
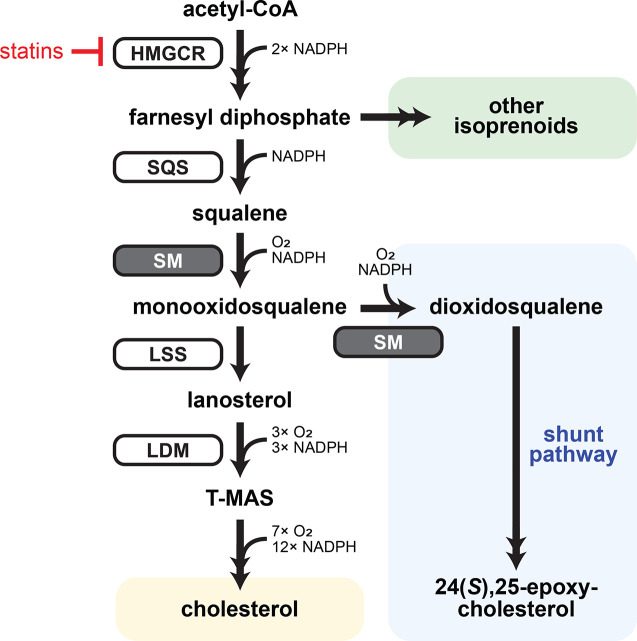
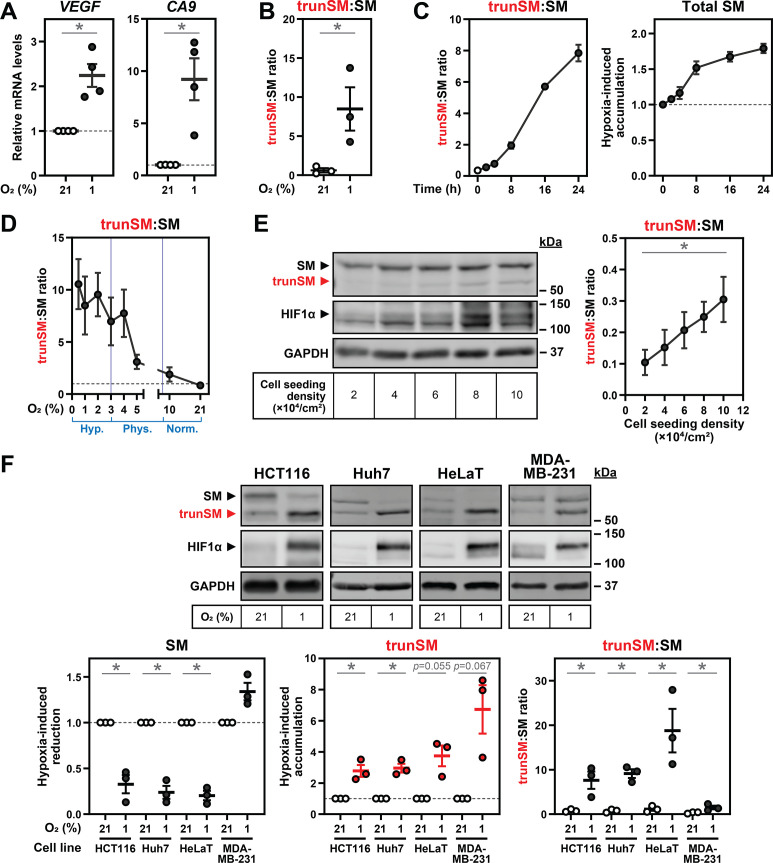
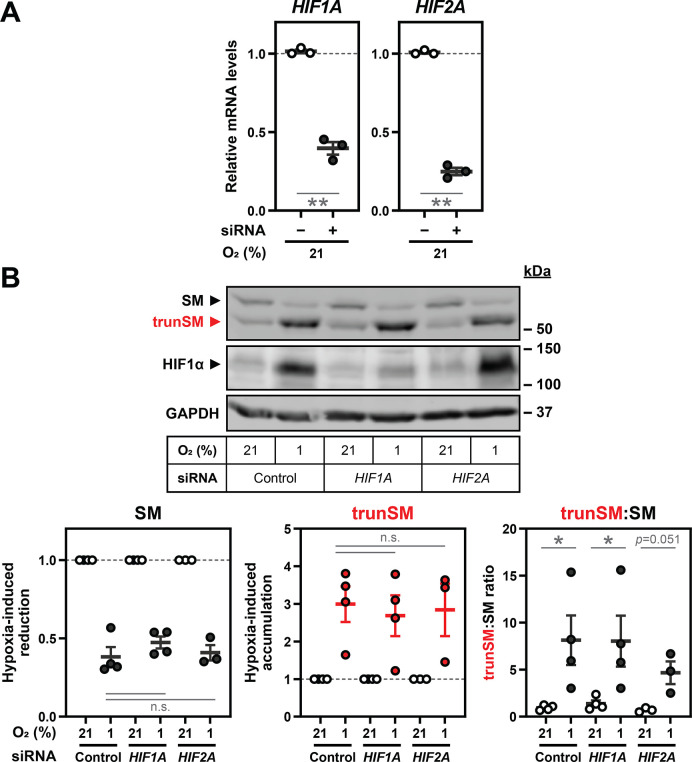
Figure 1. Oxygen availability regulates SM truncation.
(A) Simplified overview of SM truncation. Full-length SM contains an N-terminal domain mediating feedback regulation by cholesterol. Ubiquitinated SM is targeted to the proteasome, where proteolysis is prematurely halted within the regulatory domain. This liberates a truncated protein (trunSM) that no longer responds to cholesterol and is therefore constitutively active. (B) HEK293T cells were incubated under normoxic (21% O2) or hypoxic (1% O2) conditions for 24 hr. (C) HEK293T cells were incubated under normoxic or hypoxic conditions for the indicated times. Changes in HIF1α levels over time are consistent with other reports (Jantsch et al., 2011; Bartoszewski et al., 2019). (D) HEK293T cells were incubated under the indicated oxygen concentrations for 24 hr. Each set of immunoblots was obtained in a separate experiment. (B–D) Immunoblotting was performed for SM and trunSM (red). Graphs depict densitometric quantification of SM and trunSM protein levels normalized to the normoxic condition, which was set to 1 (dotted line). In (D), oxygen concentrations considered hypoxic (hyp.), ‘physoxic’ (phys.) or normoxic (norm.) (McKeown, 2014) are indicated in blue. Data presented as mean ± SEM from n=3–4 independent experiments (**, p≤0.01; two-tailed one-sample t-test vs. hypothetical mean of 1).