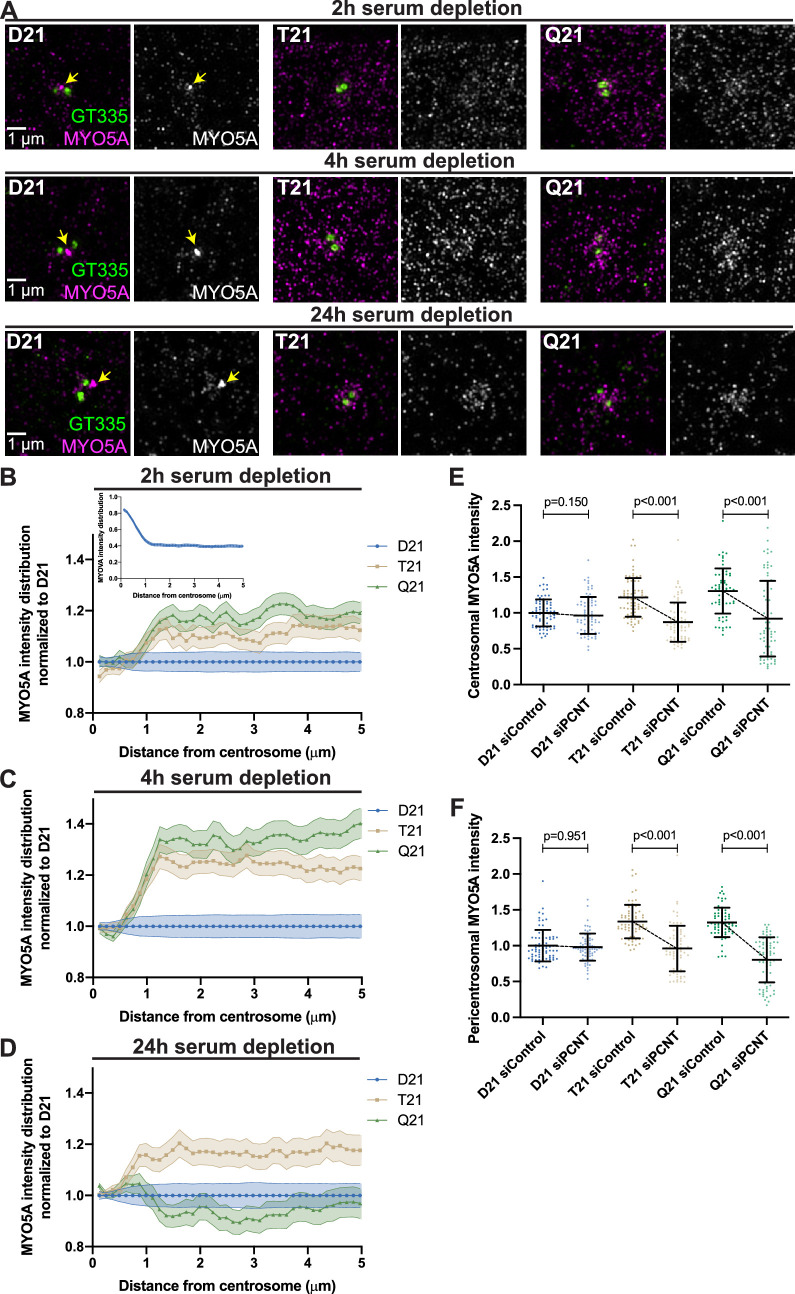
Figure 3. Preciliary vesicle components contribute to PCNT-induced pericentrosomal crowding.
(A) Representative structured illumination microscopy images from time course experiments of RPE1 D21, T21, and Q21 cells grown on coverslips and serum depleted for 2, 4, and 24 hr. Cells were stained with GT335 to label centrioles and MYO5A. (B–D) Distribution of MYO5A intensities around the centrosome for 2 (B), 4 (C), and 24 (D) hr timepoints. All values were normalized to D21 at 0 µm. Inset in (B) shows MYO5A intensity distribution in D21 cells prior to normalization. Graphs show mean ± SD. N=3. (E) Quantitation of centrosomal MYO5A intensity in 0–1.2 µm region around the centrosome for control and siPCNT treated D21, T21, and Q21 cells. Cells were treated with siControl or siPCNT for 24 hr concurrent with serum depletion. All values were normalized to the D21 siControl average. Graph show mean ± SD. N=3. Mann-Whitney U test. (F) Quantitation of pericentrosomal MYO5A intensity in 1.2–5 µm region around centrosome for control and siPCNT treated D21, T21, and Q21 cells. Cells were treated with siControl or siPCNT for 24 hr concurrent with serum depletion. All values were normalized to the D21 siControl average. Elevated MYO5A levels are distinct from the reduction observed in the distribution analyses (D) and are likely the result of the unique conditions for each experiment. Graph show mean ± SD. N=3. Mann-Whitney U test.