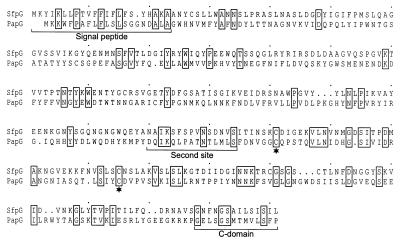
FIG. 4.
Sequence comparison between SfpG and PapGF13 (36). The alignment was produced using CLUSTAL W. Identical amino acid residues are depicted by boxes. The predicted signal peptide as well as the sites responsible for the interaction between PapG and the periplasmic chaperone (second site and C domain) are indicated by the brackets. Conserved pairs of cysteine residues in the C-terminal protein domain are marked by asterisks.