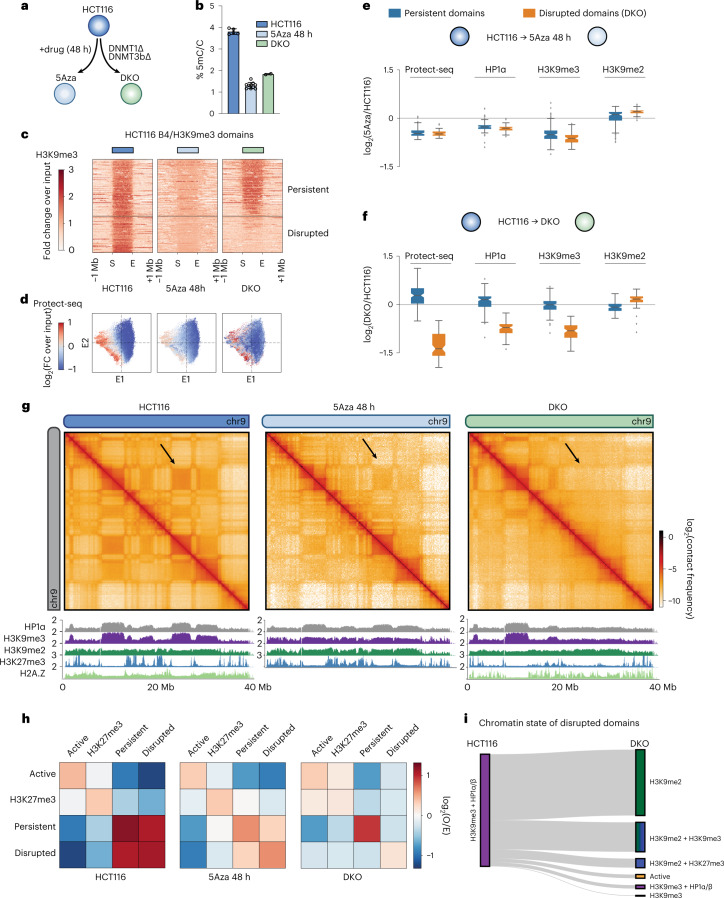
Fig. 5. Inhibition or knockout of DNA methyltransferases disrupts H3K9me3-HP1α/β heterochromatin and compartmentalization.
a, Schematic of the DNA methylation perturbation system used in this study. b, LC–MS quantification of 5-methylcytosine/total cytosine for HCT116 (left, n = 5 biological replicates), HCT116 cells treated with 5Aza (48 h) (middle, n = 10) and DNMT1/DNMT3b knockout (DKO) (right, n = 2) cells. Data are presented as mean values with ±s.d. error bars. c, Stacked heatmaps of H3K9me3 ChIP–seq signal in HCT116 (left), 5Aza 48 h (middle) and DKO (right) centered at uniformly rescaled B4 domains, sorted vertically by the intradomain H3K9me3 ratio between DKO and HCT116, and partitioned into two categories: persistent domains (top) and disrupted domains (bottom) in DKO. d, Scatter plots of 50-kb bins along E1 versus E2 (HCT116 eigenvectors), colored by Protect-seq signal for HCT116 (left), 5Aza 48 h (middle) and DKO (right). e, Box plots quantifying the distribution of log2 ratios of mean domain signal between HCT116 and 5Aza in persistent (left, n = 185) and disrupted (right, n = 116) B4 domains. Signals shown are Protect-seq, HP1a, H3K9me3 and H3K9me2. Box extents give the interquartile range with whiskers extending by a factor of 1.5 and the notch representing the confidence interval around the median. Points represent outliers. f, Same as e but between HCT116 and DKO. g, Contact frequency maps of a 40-Mb genomic region (chr9:0–40 Mb) in HCT116 (left), 5Aza 48 h (middle) and DKO (right) containing representative examples of persistent and disrupted domains. Below, ChIP–seq tracks for H3K27me3, H3K9me2, H3K9me3, HP1α and H2A.Z. h, Heatmap displaying the pairwise mean observed/expected contact frequency between active, H3K27me3 and H3K9me3 domains split into either disrupted or persistent labels in DKO based on ChromHMM states learned at 50 kb. i, Sankey plot of disrupted domains illustrating the chromatin transition from H3K9me3-HP1α/β in HCT116 cells to H3K9me2 and/or other repressive states based on ChromHMM in DKO cells.