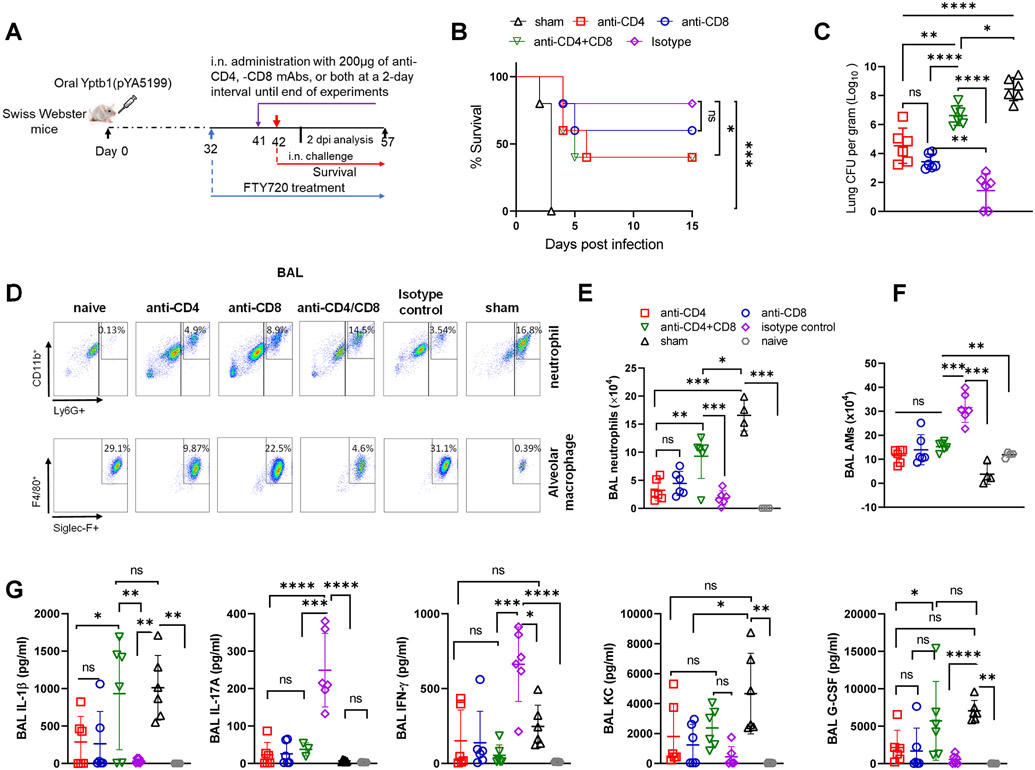
Figure 4. Local depletion of lung resident CD4+ and/or CD8+ T cells in Yptb1(pYA5199)-immunized mice impairs protection against pneumonic plague.
(A) Scheme of immunization, FTY720 treatment, T-cell depletion, and survival against pneumonic plague infection. (B) Survival study in the lung T cell-depleted mice. The Yptb1(pYA5199)+FTY720-immunized mice (n=6 females) were depleted of CD4+ and/or CD8+ T cells at the lung mucosal site by i.n. administration of 200 μg of anti-CD4, anti-CD8, or both mAbs and then intranasally challenged with 50 LD50 of Y. pestis. (C) Lung Y. pestis burden at 2 dpi (n= 5 females). (D) Representative flow plots showing the percentages of neutrophils and alveolar macrophages in the BAL fluid at 2 dpi. (E) The number of neutrophils and (F) alveolar macrophages (AMs) in the BAL fluid of control and T cell-depleted mice (n= 6 females) at 2 dpi. (G) Analysis of cytokines and chemokines in the BAL fluid samples collected at 2 dpi. Each symbol represents a data point obtained from an individual mouse. The statistical analysis is described in the Materials and Methods.