Figure 2: In-Hospital Mortality of Cardiogenic Shock by SCAI Stage Across Staging Methods.
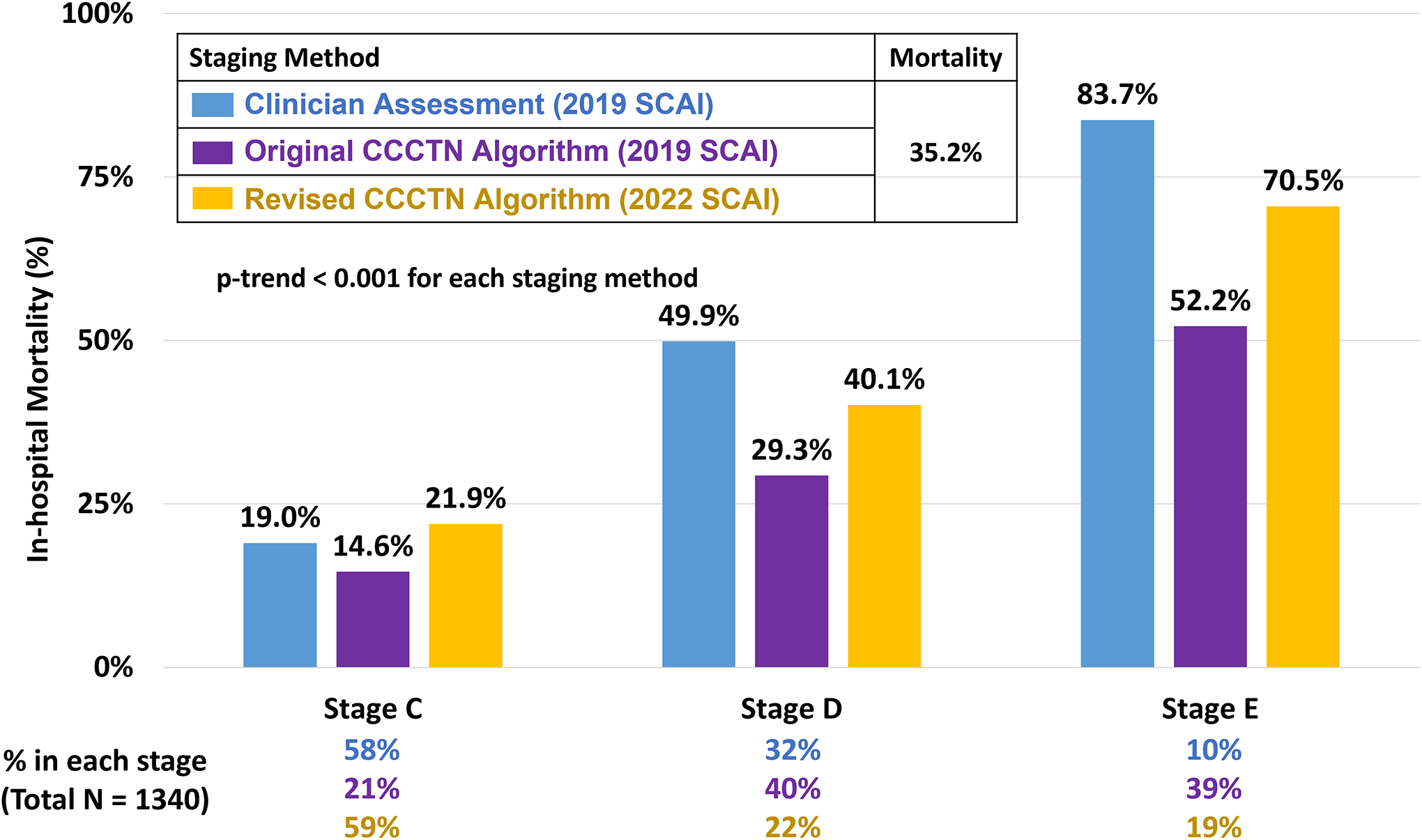
Consecutive CICU admissions with CS were assigned shock staging using all three methods: clinician assessment based on the 2019 SCAI CS stages (blue), CCCTN algorithmic application of the 2019 SCAI CS stages (purple), and CCCTN algorithmic application of the 2022 SCAI CS stages (yellow). Each staging method effectively identified a stepwise gradient of risk for in-hospital mortality (p-trend < 0.001 for each), though clinicians identified higher risk patients for allocation to the advanced SCAI stages (stages D and E). CCCTN algorithmic application of the 2022 SCAI shock stages, with incorporation of the vasoactive-inotropic score, refined original algorithm-based staging and more closely approximated clinician application. CCCTN = Critical Care Cardiology Trials Network; CS = cardiogenic shock; SCAI = Society of Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions.
