Figure 3.
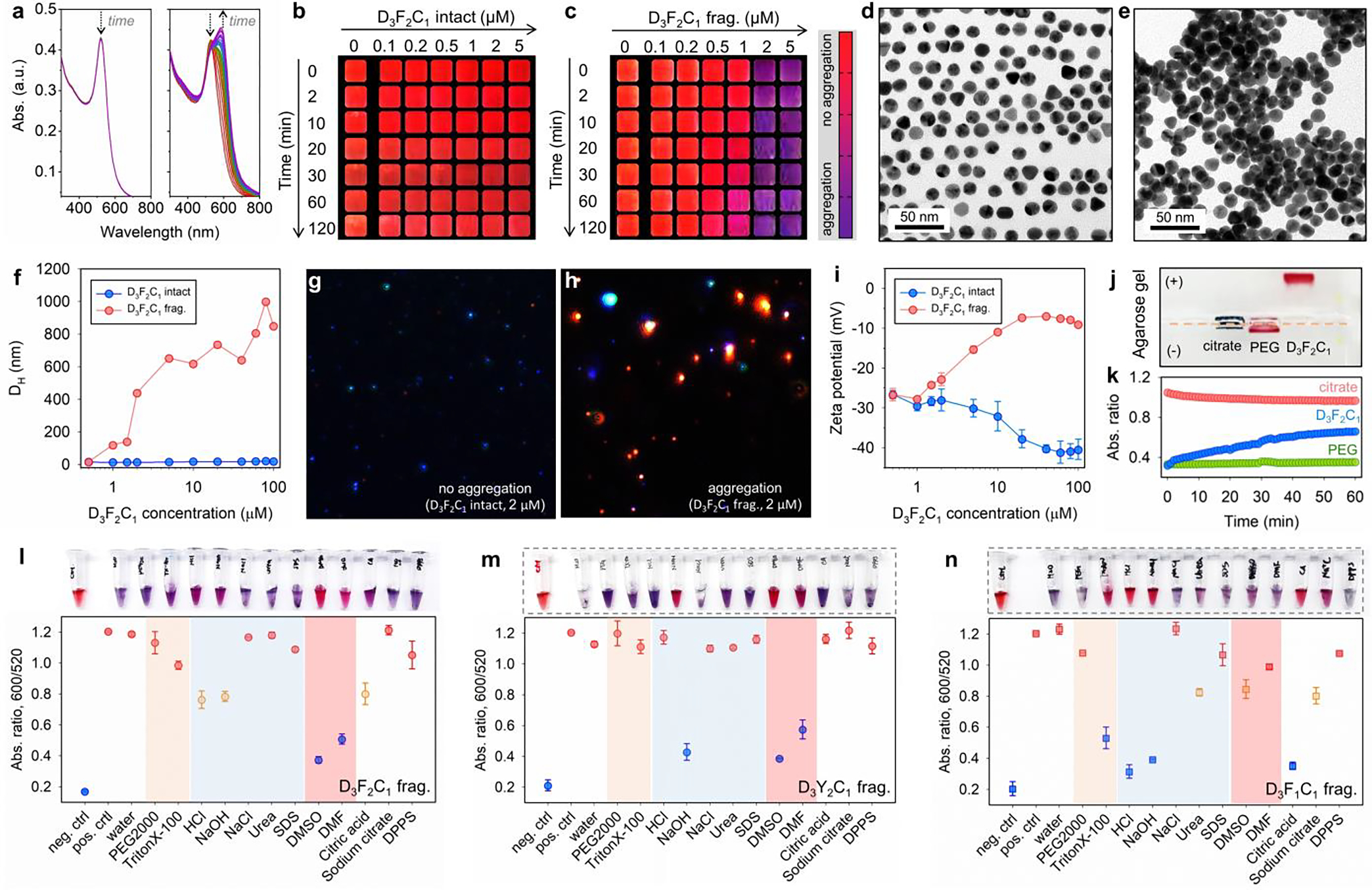
Mpro-induced color change using the modular peptide amphiphiles and colloidal gold (citrate). (a) The time progression of optical absorption of AuNPs (3.4 nM, 100 μL) when incubated with D3F2C1 intact (left) and its fragments (right, c = 1.5 μM). The curves were recorded every 1 min for 30 min. Arrows designate sizable optical changes at 520 and 600 nm. (b-c) The concentration- and time-dependent color evolution of AuNPs (3.4 nM, 100 μL) in the presence of intact D3F2C1 and its pre-cleaved fragments. These are cropped images with a color bar where purple represents particle flocculation. See also TEM images of AuNPs (3.4 nM, 8 μL) when mixed with D3F2C1 intact (d, monolayer) and its fragments (e, heterogeneous stacking). (f) DLS profiles of AuNPs (3.4 nM, 100 μL) incubated with D3F2C1 intact (blue) and its fragments (red) of 0 – 100 μM. (g-h) View of MANTA[22b] size measurement shows that AuNPs (c = 0.2 – 0.6 nM) scatter blue light with D3F2C1 intact (2.0 μM), whereas the fragment-induced colloidal aggregates scatter red light. (i) Zeta potential of AuNPs (3.4 nM, 100 μL) when incubated with increasing concentrations of D3F2C1 intact (blue, reduced from −26.0 to −40.4 mV) and its fragments (red, increased from −26.6 to −9.0 mV). Error bars represent triplicate measurements for one sample. (j) The agarose gel (0.7% w/v) electrophoresis image collected from citrate-AuNPs only, AuNPs incubated with HS-PEG2k-OCH3, and intact D3F2C1 (from left to right). Samples were prepared using the AuNPs (~15 nM, 40 μL) mixed with glycerol (10 μL). Note that TBE buffer (1×) promotes instant aggregation of citrate-AuNPs. (k) Ca2+ cation (20 mM)-modulated dispersity of citrate (red), PEGylated (green), and D3F2C1-capped AuNPs (blue). The colloidal dispersity is quantified by ratiometric signal, i.e., Abs600/Abs520. The DDD stretch negatively charges the surfaces and promotes colloidal stability via electrostatic double repulsion. (l-n) White-light image (top) and quantified reversal color change (bottom) of the gold pellet in different surfactant solutions (10 mM, 100 μL) or solvents (100 μL). Panel l indicates an aromatic stacking-driven co-assembly of D3F2C1 fragments and AuNPs. The gold pellet is prepared by aggregating AuNPs (3.4 nM, 100 μL) with D3F2C1/D3Y2C1/D3F1C1 fragments (at 600 μM, 30 μL). Error bars = standard deviations (n = 3).
