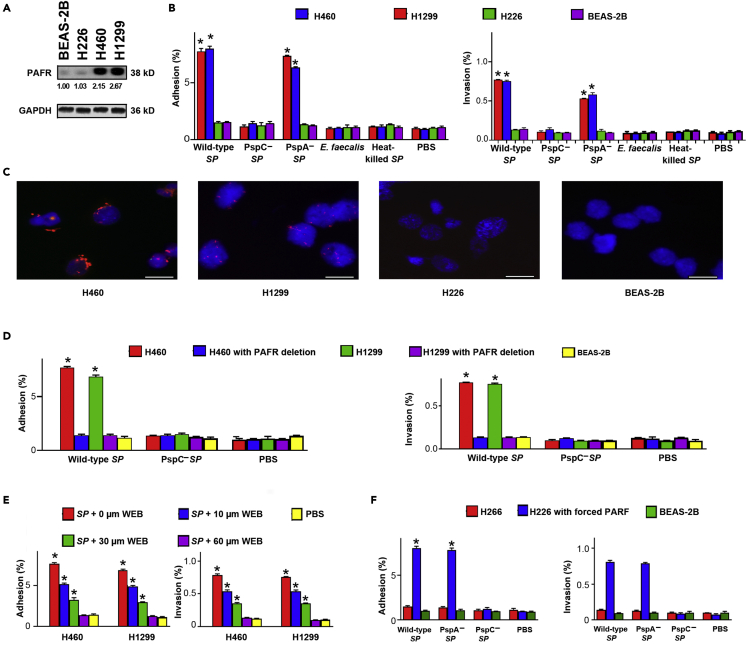
Figure 1.
SP attaches to and invades lung cancer cells via binding PspC to PAFR
(A) PAFR expression was determined in cancer cell lines (H226, H460, and H1299) and a normal lung epithelial cell line (BEAS-2B) by Western blot. GAPDH was used as the loading control. Band intensity was determined by using ImageJ, and the ratio of each band was normalized to the corresponding GAPDH and shown below each band. H460 and H1299 cells had a higher level of PAFR expression compared with H226 cells and BEAS-2B cells. Data presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3); ∗p < 0.01 by one-way ANOVA.
(B) SP adhered to and invaded the PAFR-expressing cells (H226 and H1299). Bacteria were added to cells at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 10 for 1 h. The PspC-deficient mutant SP and heat-killed SP were defective for attachment and invasion compared to wild-type SP and the PspA-deficient mutant SP. E. faecalis did not attach to and invade lung cancer cells. Cells treated with PBS were used as negative controls. Data presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3); ∗p < 0.01 by one-way ANOVA.
(C) FISH analysis of SP using an Alexa Fluor 594-conjugated specific probe (Red) to SP. 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) was used to visualize nuclear DNA of cells. Original magnification, X400. Three independent experiments were performed with consistent results. H460 and H1299 cells showed positive staining for SP (Red signals). Scale bar, 10 μm.
(D) The depletion of PAFR in H460 and H1299 cells by using siRNA reduced attachment and invasion of SP. Data presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3); ∗p < 0.01 by one-way ANOVA.
(E) The PAFR inhibitor, WEB2086, suppressed attachment and invasion of SP to H460 and H1299 cells in a dose-dependent manner (10, 30, and 60 μM and 1,000 μM WEB2086 were used). ∗p < 0.01.
(F) Enforced expression of PAFR in H226 cells increased attachment and invasion of wild-type SP and PspA-deficient mutant SP, but not PspC-deficient mutant SP. All the results are presented as the mean ± SD of three different experiments with triplicates. Data presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3); ∗p < 0.01 by one-way ANOVA.