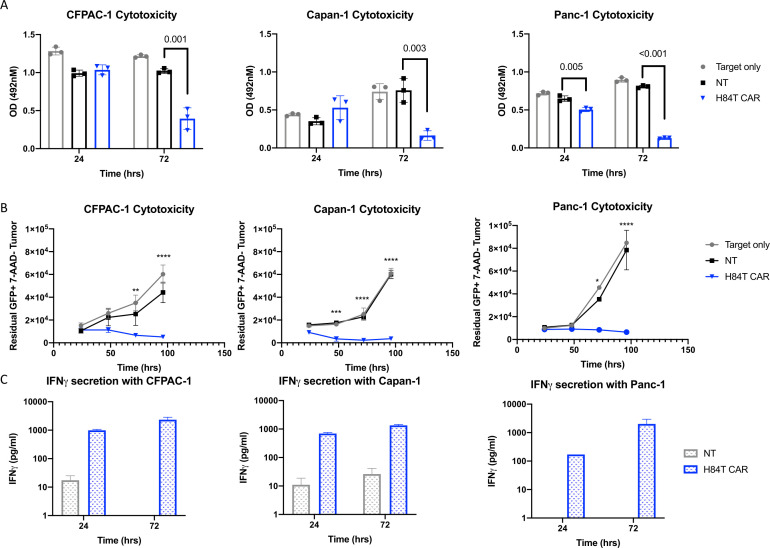
Figure 3.
Antitumor activity of H84T CAR T cells against PDAC tumor cell lines. (A) 4×104 PDAC tumor cell lines were seeded in 96-well plates and 1×104 NT or H84T CAR T cells were added. Tumor cell viability was determined by MTS assay at 24 hours and 72 hours post T-cell addition. Optical density (OD) values were obtained at 492 nm wavelengths. Averages of three technical triplicates of three different donor T cells are represented. P values determined by unpaired student’s t-test. (B) Co-culture of PDAC tumor cell lines with NT or H84T CAR T cells at a 4:1 ratio. Residual viable tumor cells labeled with GFP firefly luciferase were quantified by flow cytometry, 7-AAD staining and absolute counting beads. Samples were collected at 24, 48, 72, and 96 hours post T-cell addition. n=3–4 donors per cell line. P values determined by two-way analysis of variance comparing NT versus H84T; *p<0.05; **p<0.005;***p<0.0005; ****p<0.0001. (C) Supernatant from PDAC tumor cell lines cultured with NT or H84T CAR-T cells were collected 24 and 72 hours post T-cell addition (1:4 effector:target ratio). IFN-γ secretion was measured by ELISA assay. Average of three donors are represented. MTS, Tetrazolium Assay, 7-AAD; 7-aminoactionomycin D; CAR, chimeric antigen receptor; GFP;green fluorescent protein; IFN, interferon; PDAC, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; NT, non-transduced.