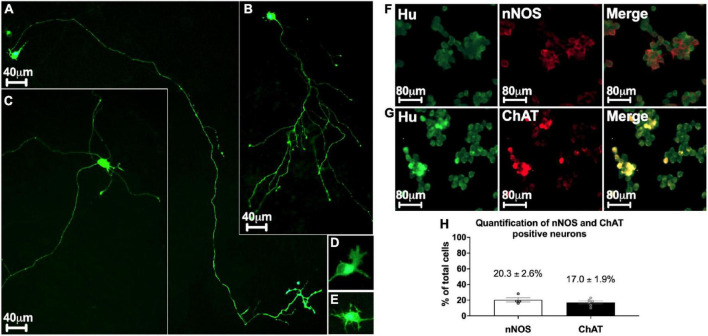
FIGURE 3.
Morphological and phenotypical characterization of enteric neurons. (A–E) mGFP transfected enteric neurons at D3. (A,B) Monoaxonal enteric neurons with a small-diameter cell body. Monoaxonal neurons can be sorted into two sub-types based on axon morphology: long axonal process with sparse and short ramifications (A) or medium-length axon with numerous ramifications (B). (C) Multiaxonal neurons exhibiting more than 2 axons of medium to short length and a large-diameter cell body (183 neurons analyzed from n = 4 culture wells from 4 independent rat embryos). (D,E) Neuron with lamellar (D) and filamentous (E) dendrites (110 neurons analyzed from n = 3 culture wells from 3 independent rat embryos). (F,G) Double immunostaining of enteric neurons with the neuronal cell body marker Hu (green) with either nNOS (red, F) or ChAT (red, G) at D7. (H) Percentage of neurons immunostained with neuronal nNOS and ChAT at day 7. Data are presented as mean ± SEM from 886 neurons analyzed from n = 4 culture wells from 4 independent rat embryos.