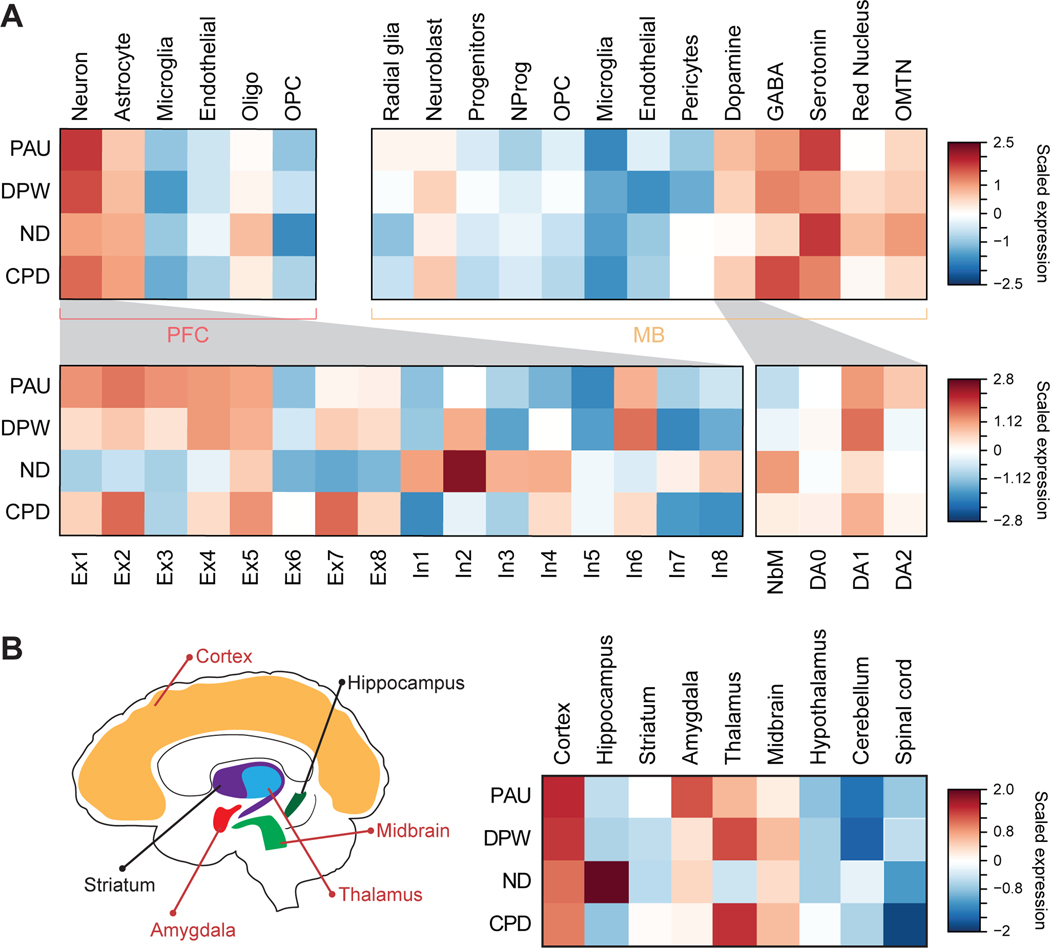
Figure 3. Cellular and brain regional expression profiles of cigarette smoking and alcohol use risk genes.
A. Top left panel represents cellular expression profiles of cigarette smoking and alcohol use risk genes identified from CN H-MAGMA using scRNA-seq data from the adult cortex[46, 70]. Genetic risk factors underlying cigarette smoking and alcohol use influence genes highly expressed in neurons. Bottom left panel represents risk gene expression across neuronal subclusters. OPC, oligodendrocytes progenitor cells; Ex, excitatory neurons; In, inhibitory neurons. Top right panel, cellular expression profiles of cigarette smoking and alcohol use risk genes identified from DN H-MAGMA using scRNA-seq from the ventral midbrain of human embryo. Risk genes are highly expressed in dopaminergic, GABA-ergic, and serotonergic neurons in the midbrain. NProg, neuronal progenitors; OMNT, oculomotor and trochlear nucleus. Bottom right panel, cigarette smoking and alcohol use risk genes were enriched for DA1 across DN development in human embryonic midbrain. NbM, medial neuroblasts and precursors of DNs; DA0, immature DNs; DA1, intermediate DNs; DA2 matured DNs. B. Left, graphic representation of brain regions with elevated expression levels of risk genes for substance use traits. Regions highlighted in red are enriched for at least three of the four traits. Right, brain regional expression profiles of cigarette smoking and alcohol use risk genes using scRNA-seq from the mouse nervous system[23]. Risk gene expression spans multiple brain regions including the cortex, amygdala, and midbrain.