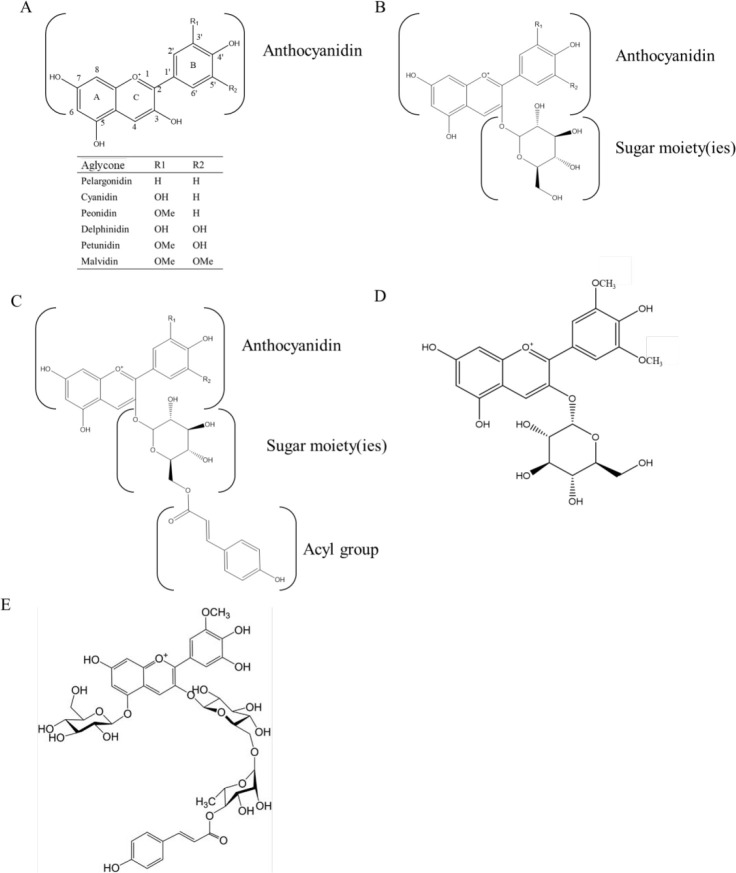
Figure 1.
Structures of common anthocyanins. An example of nonacylated and acylated anthocyanins. Glucose is attached to the C3 position of anthocyanidin (A) to form nonacylated anthocyanin (B). Based on nonacylated anthocyanin, p-coumaric acid is acylated with a glucose residue at the C6 position to form acylated anthocyanin (C). Malvidin-3-O-glucoside (D). Petunidin-3-O-[6-O-(4-O-E-p-coumaroyl-O-α-l-rhamnopyranosyl)-β-d-glucopyranoside]-5-O-β-d-glucopyranoside (E), adapted with permission from ref (105). Copyright 2003 Elsevier.