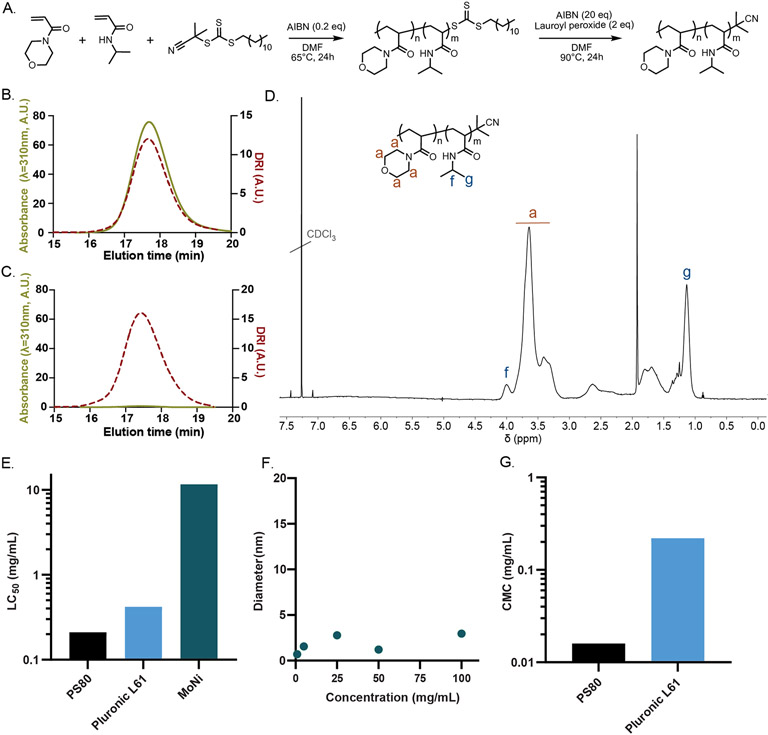
Figure 2. Synthesis and characterization of MoNi copolymer excipient.
(A) Synthetic scheme for the synthesis of poly(acryloylmorpholine-co-N-isopropylacrylamide) (MoNi). Size exclusion chromatography (SEC) characterization of the (B) MoNi-CTA (chain transfer agent) intermediate and (C) MoNi demonstrates that the CTA is completely removed in the second step of the synthesis, yielding a chemically stable copolymer. (D) 1H-NMR characterization of MoNi. (E) Comparison of cytotoxicity of MoNi[15], polysorbate 80[16], and pluronic L61[17]. (F) DLS characterization of MoNi in solution at various concentrations. (G) Comparison of critical micelle concentration (CMC) values for polysorbate 80[18], and pluronic L61[19]. MoNi did not exhibit micelle formation within the assessed concentration range (100 to 1 mg/mL).