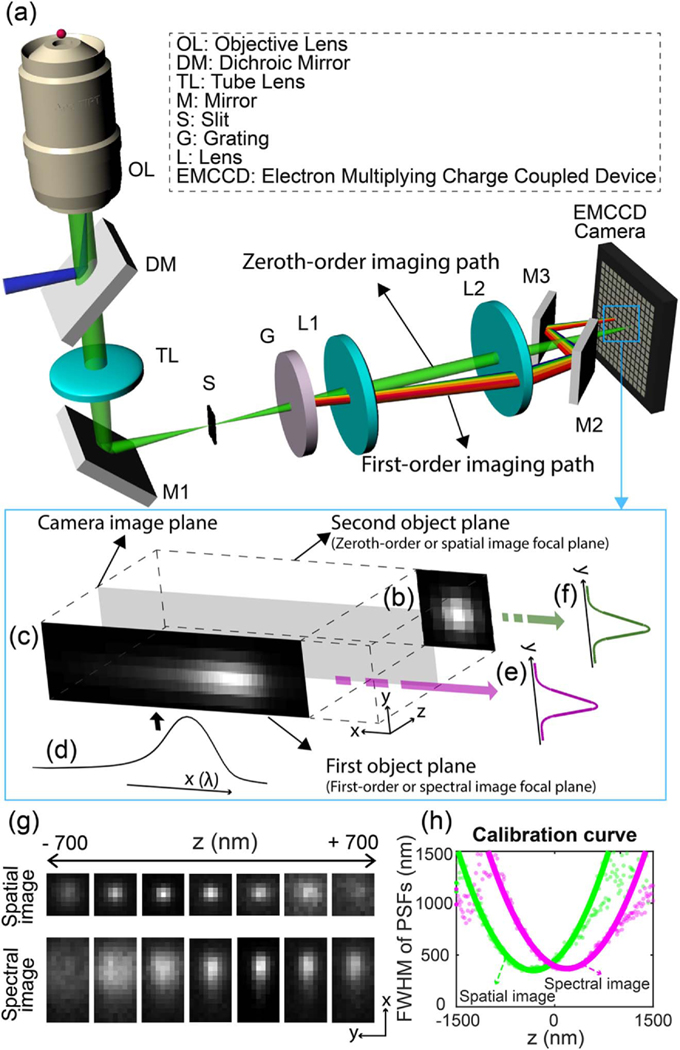
Fig. 1.
(a) Schematic and (b–f) working principle of 3D biplane sSMLM. (b) The detected spatial image and (c) the spectral image of a single-molecule emission. (c) The spectral image is the result of the convolution of the diffraction-limited PSF of individual stochastic fluorescent-emitting molecules in the spectral imaging plane and (d) the linearly spread spectroscopic signature. By integrating the spectral and spatial images along the x axis, (e), (f) 1D PSFys are retrieved from both images and used for biplane imaging. (g) The experimentally acquired spatial (top row) and spectral (bottom) images at the different axial positions from single emitters. (h) The experimentally obtained depth calibration curve.