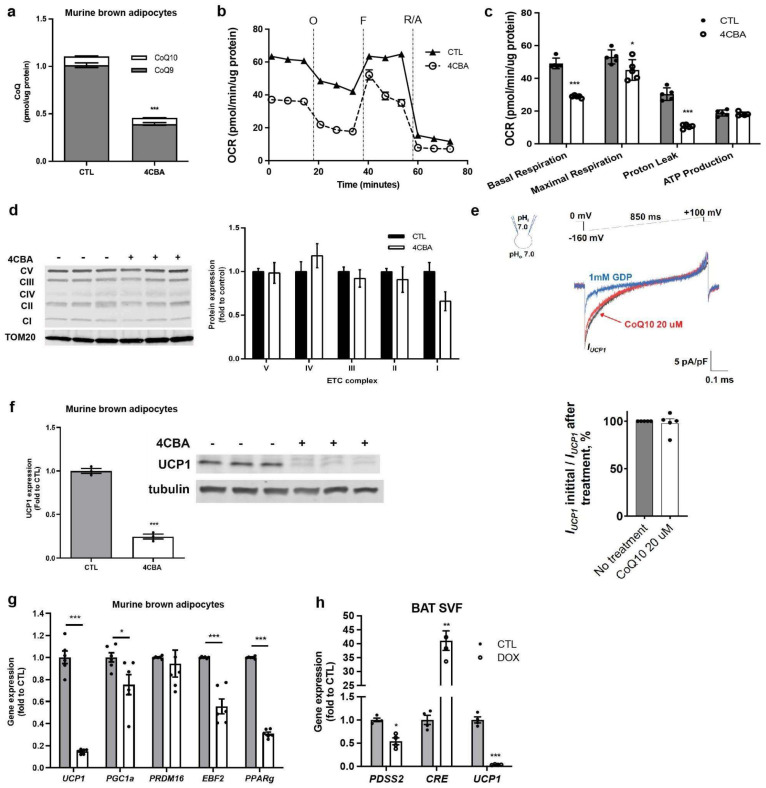
Figure 1.
CoQ deficiency affects BAT mitochondrial respiration and UCP1 level. (a) Coenzyme Q (CoQ) levels in murine brown adipocytes were decreased after treatment with 4-chlorobenzoic acid (4CBA) compared to vehicle (CTL), n = 3. (b,c) Oxygen consumption rate (OCR) was measured in control, and 4CBA treated cells, using seahorse XFe24 analyzer and components of mitochondrial respiration were analyzed, n = 5. Basal, maximal, and proton leak OCR were decreased in 4CBA-treated cells compared to CTL. (d) Mitochondrial complexes isolated from brown adipocytes were measured by western blot, n = 3. Expression was unchanged between CTL and 4CBA-treated cells. Each lane in the western blot pictured is one independent sample. (e) Upper panel: Representative UCP1-dependent H+ current recorded from whole brown fat mitoplasts before (black) or after CoQ10 treatment (20 µM). 1 mM GDP (blue) was used as an inhibitor of UCP1 activity. Lower panel: UCP1-dependent H+ current densities in the inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM) of brown fat after CoQ10 treatment compared to UCP1-dependent H+ current before treatment, n = 5. No differences were observed in H+ current densities between CTL and CoQ10-treated samples. Mean ± SEM. (f) UCP1 protein expression in murine brown adipocyte cells, measured by western blot, was decreased in 4CBA-treated cells compared to CTL, n = 3. (g) Thermogenic genes were measured by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (rtPCR), n = 6. UCP1 gene expression was decreased in 4CBA-treated cells. (h) Stromal vascular fraction (SVF) was isolated from brown adipose tissue (BAT) of PDSS2FL animals, and PDSS2 was knockout by the induction of cre recombinase with doxycycline. Gene expression was measured by rtPCR, n = 4. PDSS2 and UCP1 gene expression was decreased while Cre expression was increased. Data are mean ± SEM. Significance presented at * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.001 compared to controls or otherwise indicated.