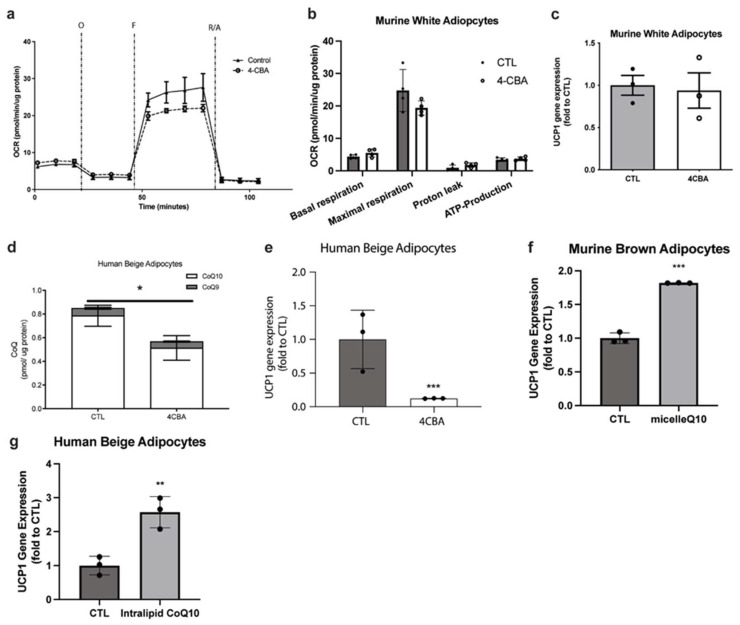
Figure 2.
CoQ deficiency does not affect white adipocyte respiration and UCP1 levels. CoQ supplementation restores UCP1 levels in murine brown adipocytes and human beige adipocytes. (a,b) OCR of white murine adipocytes, which remained unchanged between CTL and 4CBA treated cells, were measured using a seahorse XFe24 analyzer, and components of mitochondrial respiration were analyzed, n = 4. (c) UCP1 gene expression, measured using rtPCR, was not significantly changed in white murine adipocytes treated with 4CBA compared to CTL. (d) CoQ levels were decreased in human beige adipocytes treated with 4CBA compared to CTL, n = 3. Data are mean ± SEM. (e) UCP1 gene expression of human beige adipocytes, measured using rtPCR, treated with 4CBA was decreased compared to CTL. (f) UCP1 gene expression in murine brown adipocytes treated with a micellar formulation of CoQ10 (n = 3) and (g) UCP1 gene expression in human beige adipocytes treated with an intralipid formulation of CoQ10 (n = 3), measured using rtPCR, was increased compared to cell treated with vehicle (CTL). Data are mean ± SEM. Significance presented at * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.001 compared to controls or otherwise indicated.