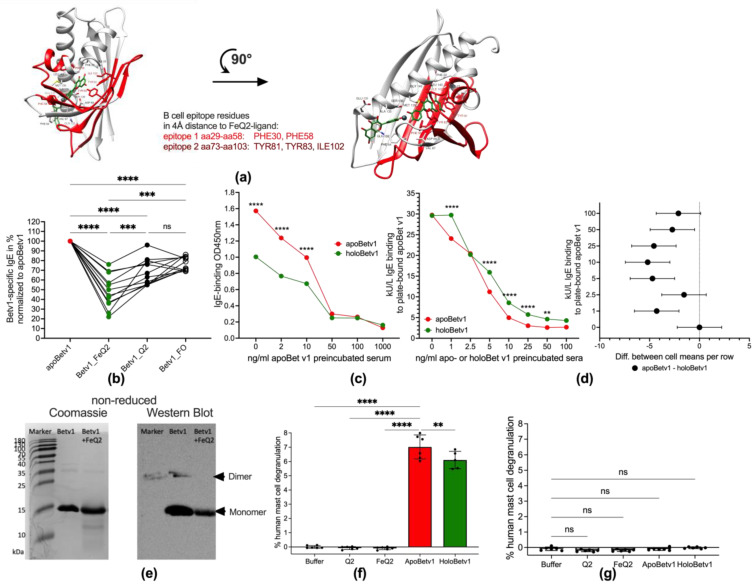
Figure 2.
Binding of iron—quercetin complex by Bet v 1 masks B cell epitopes and affects IgE binding and mast cell degranulation (a): Structure of Bet v 1—Fe(quercetin)2 complex shown as cartoon from two different views. Iron complexed by two quercetins (FeQ2) is depicted as sticks with carbons in green and oxygens in red. Iron atom (Fe) is represented as a grey sphere. Major B-cell epitope 1 (29–58) and epitope 2 (73–103) are marked in light and dark red, respectively. Residues within a 4Å distance from any atom of FeQ2 are shown as sticks with carbons in red. (b): Serum IgE binding of birch pollen allergic (n = 12) to Bet v 1 without cargo (apoBet v 1) or in combination with iron-quercetin (Bet v 1_FeQ2), quercetin (Bet v 1_Q2), or ferroxamine (Bet v 1_FO). (c): Blocking experiments with pooled birch pollen allergic incubated with increasing doses of apo Bet v 1 and binding to plate-bound apo- (red line) or holoBet v 1 (green line). (d): Summary and confidence interval plot of blocking experiments incubating 6 individual sera of birch pollen allergic subjects with increasing doses of apo- or holoBet v 1 and assessing IgE binding to plate-bound apoBet v 1. (e): Protein bands stained by Coomassie and serum IgE binding against Bet v 1 alone or in combination with FeQ2 of gels run under non-reducing conditions. Degranulation of human mast cells sensitized with pooled (f) birch pollen allergic (g): non-allergic sera. For statistical analyses (b) was compared with RM one-way ANOVA with Geissner Greenhouse correction and Holm-Sidák’s multiple comparisons test (c,d) with two-way ANOVA using Holm-Sidák’s multiple comparisons test, with a single pooled variance, (f) with mixed-effect analyses using the Geissner Greenhouse correction and Holm-Sidák’s multiple comparisons test, (g) with one-way ANOVA following Holm-Sidák’s multiple comparisons tes. Mean ± SD; ns not significant, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001.