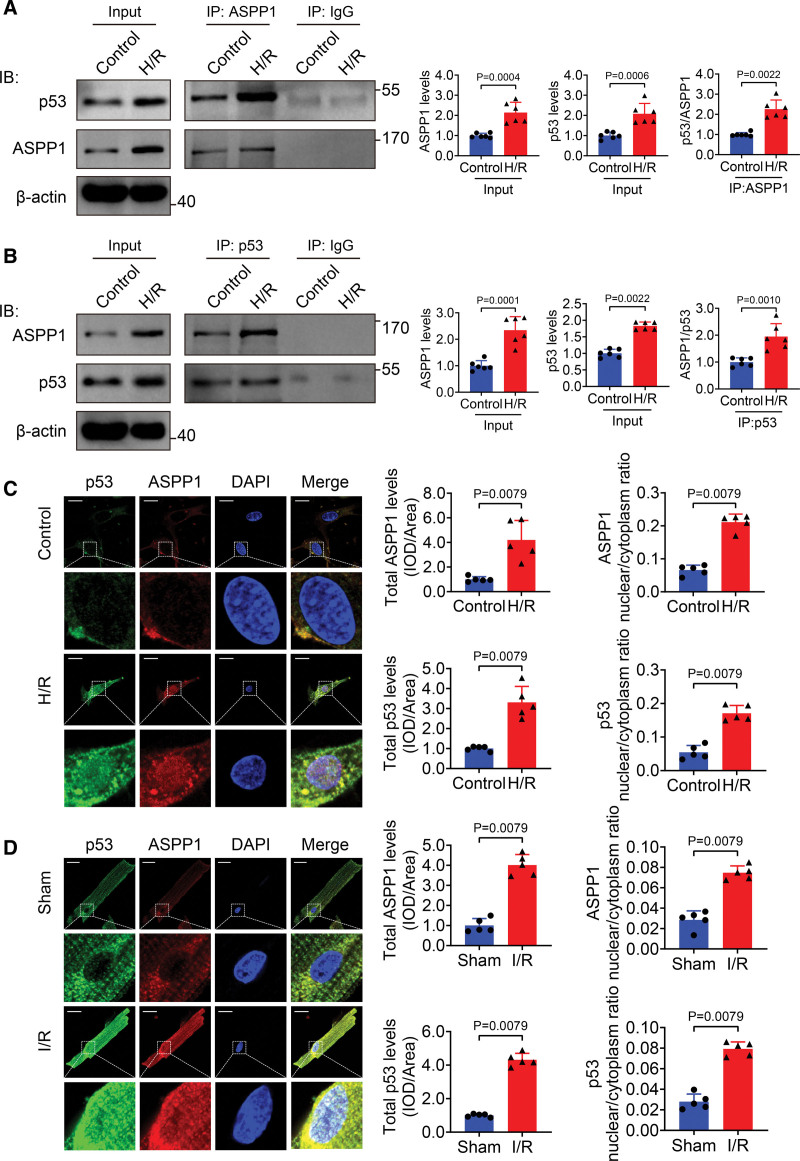
Figure 1.
Nuclear cotranslocation of ASPP1 and p53 in cardiomyocytes during cardiac ischemia reperfusion injury. A, Proteins from cultured neonatal mouse ventricular cardiomyocytes (NMVCs) subjected to control or 12 hours hypoxia followed by 24 hours reoxygenation (H/R) treatment were immunoprecipitated with ASPP1 or IgG antibody, followed by Western blot; n=6. Statistical significance was assessed by Mann-Whitney U test (p53/ASPP1) or Student t test (ASPP1 levels and p53 levels). B, Proteins from NMVCs were immunoprecipitated with p53 or IgG antibody followed by Western blot; n=6. Statistical significance was assessed by Mann-Whitney U test (ASPP1 levels) or Student t test (p53 levels and ASPP1/p53). C and D, Immunostaining assay was used to analyze the colocalization of ASPP1 and p53 in H/R NMVCs and isolated adult cardiomyocytes of I/R (45 minutes ischemia followed by 24 hours reperfusion) mice (Mann-Whitney U test); n=5. Scale bar=20 μm. ASPP1 indicates apoptosis stimulating of p53 protein 1; and DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.