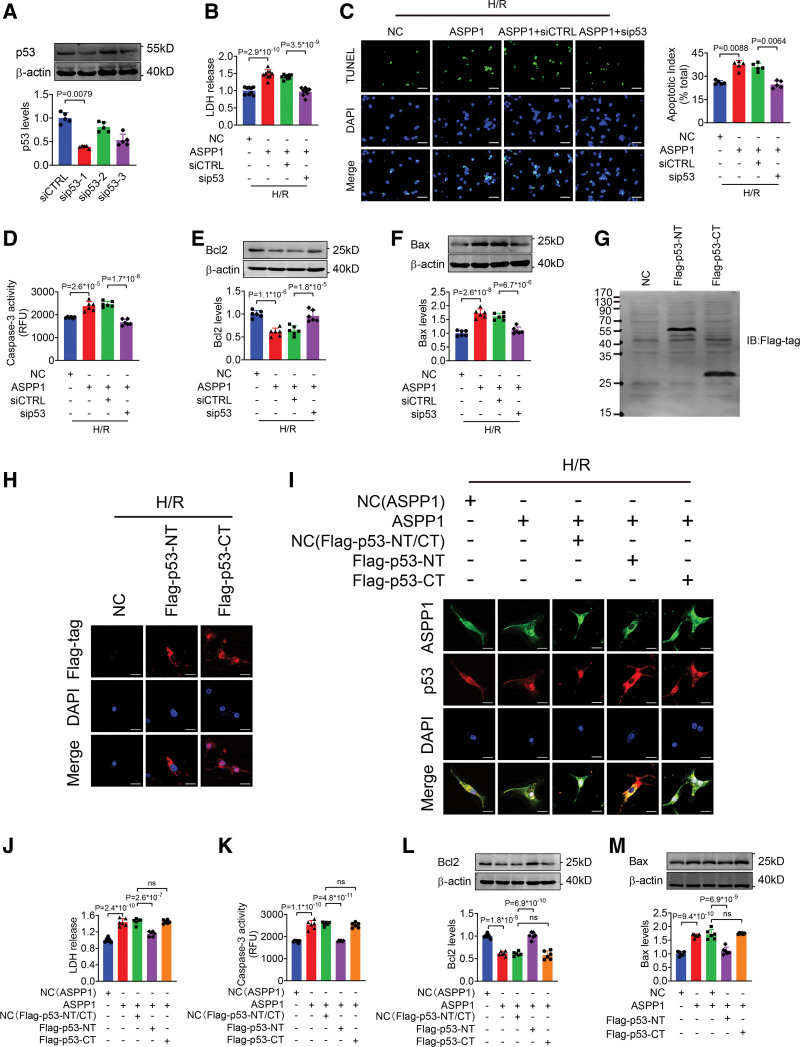
Figure 7.
p53 mediates the proapoptotic effects of ASPP1. A, The efficiency of small interfering RNA (siRNA) of p53 in neonatal mouse ventricular cardiomyocytes (NMVCs) by Western blot (Mann-Whitney U test); n=5. B, LDH release after cotransfection of siRNA of p53 and ASPP1 plasmid (1-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey post hoc multicomparisons test); n=9. C, Apoptosis index of NMVCs detected by TUNEL (TdT-mediated dUTP nick end labeling) assay (Kruskal-Wallis, followed by false discovery rate [FDR] method of Benjamini and Hochberg test); n=5. Scale bar=50 μm. Green, TUNEL- positive cells; blue, DAPI. D, Caspase-3 activity in NMVCs by ELISA assay (1-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey post hoc multicomparisons test); n=6. E and F, The protein levels of Bcl2 and Bax detected by Western blot (1-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey post hoc multicomparisons test); n=6. G, Validation of p53-NT and p53-CT by Western blot. Flag-p53-NT, N-terminal fragment containing binding domain for ASPP1 without nuclear localizing signal (NLS, 1–288 aa) and Flag-p53-CT, C-terminal fragment containing NLS of p53, which is responsible for its nuclear localization (310-381 aa); n=5. H, Celluar distribution of Flag-p53-NT and Flag-p53-CT by immunofluorescent staining; n=5. Scale bar=20 μm. I, Effects of Flag-p53-NT and Flag-p53-CT on ASPP1 and p53 nuclear translocation in NMVCs; n=5. Scale bar=20 μm. J, LDH level in culture medium after treated with Flag-p53-NT or Flag-p53-CT (1-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey post hoc multicomparisons test); n=6. K, Caspase-3 activity in NMVCs after cotransfection of Flag-p53-NT or Flag-p53-CT and ASPP1 plasmid by ELISA assay (1-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey post hoc multicomparisons test); n=6. L and M, The protein levels of Bcl2 (L) and Bax (M) after cotransfection of Flag-p53-NT or Flag-p53-CT and ASPP1 plasmid detected by Western blot (1-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey post hoc multicomparisons test); n=6. ASPP1 indicates apoptosis stimulating of p53 protein 1; Bax, Bcl2-associated X; DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; H/R, hypoxia/reoxygenation; and LDH, lactate dehydrogenase.